What is a Beta Test? A Complete Guide for Product Teams
Learn what beta testing is, why it's crucial for product success, and how to run effective beta tests to validate your product before launch.
What is a Beta Test?
A beta test is a method of testing a product, such as software or hardware, in the final stages of development before it is released to the general public according to Tempo Software. This crucial phase involves making a pre-release version available to a select group of real users who test the product in their actual environments, providing invaluable feedback that helps identify bugs, usability issues, and improvement opportunities.
Unlike internal testing conducted by developers and QA teams, beta testing represents the first time a product faces real-world usage scenarios. As ProductPlan defines it, beta testing is "an opportunity for real users to use a product in a production environment to uncover any bugs or issues before a general release."
Why Beta Testing Matters
Beta testing serves multiple critical purposes in the product development lifecycle:
- Real-world validation: Products that work perfectly in controlled development environments may encounter unexpected issues when used by actual customers in diverse settings
- User experience insights: Beta testers provide feedback on usability, workflow efficiency, and overall user satisfaction that internal teams might overlook
- Bug identification: External testers often discover edge cases and compatibility issues that internal testing missed
- Market readiness assessment: Beta testing helps gauge whether a product meets customer expectations and is ready for broader release
LaunchDarkly emphasizes that beta testing enables engineering and product management teams to "improve overall feature development to deliver features your users will love while also avoiding releasing features that either don't work or aren't used."
Types of Beta Testing
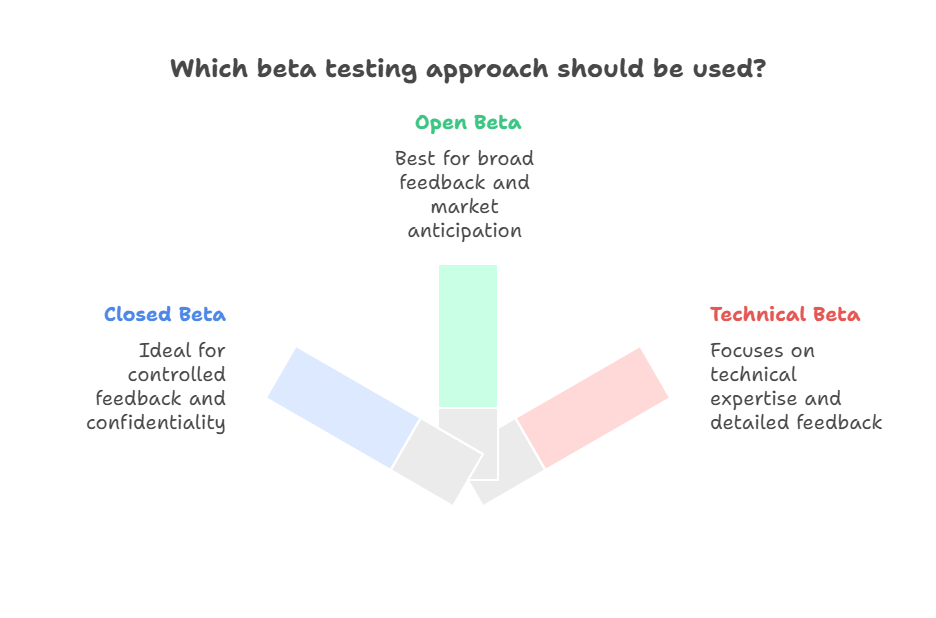
Closed Beta Testing
Closed beta tests involve a limited, invitation-only group of testers. This approach works well when you need controlled feedback from specific user segments or want to maintain confidentiality before public release.
Open Beta Testing
Open beta tests are available to anyone interested in trying the product. This approach generates broader feedback and helps build anticipation in the market before official launch.
Technical Beta Testing
Technical beta tests focus on users with specific technical expertise who can provide detailed feedback on performance, security, and integration capabilities.
The Beta Testing Process
Running an effective beta test requires careful planning and execution:
- Define objectives: Clearly outline what you want to learn from the beta test
- Select testers: Choose participants who represent your target audience
- Prepare materials: Create clear instructions, feedback forms, and communication channels
- Launch and monitor: Deploy the beta version and track usage patterns and feedback
- Collect and analyze: Gather quantitative and qualitative data from testers
- Implement improvements: Use insights to refine the product before general release
Best Practices for Successful Beta Testing
- Set clear expectations: Communicate what testers should focus on and how their feedback will be used
- Provide easy feedback mechanisms: Make it simple for testers to report issues and share insights
- Engage with testers: Maintain regular communication and show appreciation for their contributions
- Prioritize feedback: Focus on critical issues that impact user experience and product viability
- Document everything: Keep detailed records of all feedback and how it influenced product decisions
Visualizing Your Beta Testing Strategy
Creating a visual representation of your beta testing plan can help ensure all stakeholders understand the process and objectives. ClipMind offers powerful mind mapping tools that enable product teams to organize testing phases, track feedback categories, and visualize improvement priorities.
When to Conduct Beta Testing
Beta testing typically occurs after internal alpha testing but before the official product launch. The timing depends on your development cycle, but it's essential to allow sufficient time to address critical issues identified during beta testing. As GeeksforGeeks notes, beta testing involves "testing a software product or service in a real-world environment before its official release."
Measuring Beta Testing Success
Effective beta testing goes beyond simply finding bugs. Success metrics should include:
- Bug discovery rate: Number and severity of issues identified
- User satisfaction scores: Feedback on overall experience and usability
- Feature usage patterns: Which features testers use most and least frequently
- Performance benchmarks: How the product performs under real-world conditions
- Readiness assessment: Confidence level in proceeding to general release
Beta testing represents the final opportunity to validate your product with real users before public launch. By incorporating structured beta testing into your development process, you can significantly increase the chances of delivering a successful product that meets customer needs and expectations.