TL; DR
- Convert web content to mind maps for better information retention and organization
- Use ClipMind for one-click webpage summarization that eliminates manual copying and pasting
- Access full editing capabilities and export options completely free with ClipMind
- Apply noise-filtering technology to remove ads and irrelevant content before mind map generation
- Switch between dual views (Mind Map and Markdown) to accommodate different thinking styles
Introduction
I've been organizing web content for years, and like many students and professionals, I've struggled with information overload. The average person encounters dozens of webpages daily, each containing valuable information that's difficult to process and remember. Traditional note-taking methods often fail to capture the relationships between ideas, leaving us with disconnected fragments that don't support deep understanding.
This guide addresses the core challenges of web content organization by showing you exactly how to transform any webpage into a structured, visual mind map. Whether you're summarizing research papers, planning projects, or studying complex topics, you'll discover both manual techniques and AI-powered solutions that make information management efficient and effective.
What Are Webpage Mind Maps?
Webpage mind maps are visual representations of online content that capture the hierarchical relationships between main ideas and supporting details. Unlike traditional mind maps that start from a central concept you already understand, webpage mind maps extract and organize information from existing web content, creating a structured overview of someone else's thinking.
The key difference lies in the source material. Traditional mind mapping uses image-centered radial graphic organization techniques that enhance clarity and structure through non-linear scanning. Webpage mind maps apply these same principles to external content, transforming linear articles and reports into visual frameworks that reveal connections you might miss when reading sequentially.
How They Differ from Traditional Mind Maps
Traditional mind maps begin with your own central idea and branch outward as you brainstorm. Webpage mind maps work in reverse—they start with someone else's completed content and work backward to identify the core structure. This requires different skills and tools, particularly the ability to distinguish main ideas from supporting details and recognize hierarchical relationships within existing text.
The editing flexibility that makes mind maps superior to traditional notes becomes even more valuable when working with webpage content. Being able to move ideas around and draw connections between different concepts helps you reconstruct the author's thinking while making it your own.
Why Convert Webpages to Mind Maps?
The transition from linear web content to visual mind maps offers concrete benefits that impact how effectively you process, retain, and apply information. Research and practical experience consistently show that this approach transforms how we interact with digital content.
Improved Information Retention and Recall
Multiple studies demonstrate that mind mapping significantly improves knowledge retention compared to conventional learning methods. When you transform webpage content into a mind map, you're not just copying information—you're actively processing it, identifying relationships, and creating a visual structure that mirrors how your brain naturally organizes knowledge.
The technique proves particularly effective because it's an innovative method for remembering information better than routine text reading approaches. The spatial arrangement, colors, and connections in mind maps create multiple retrieval cues that make recalled information more accessible when you need it.
Better Organization of Complex Content
Many websites suffer from inadequate page structure and poor organization, making it difficult to extract the core message. Mind mapping forces you to identify the hierarchical relationships between ideas, transforming chaotic content into clearly structured knowledge.
This process addresses the common challenge of having too much content by helping you filter out non-essential information and focus on what truly matters. The visual nature of mind maps makes it immediately obvious when certain sections are overloaded or unbalanced, prompting you to reorganize for better clarity.
Enhanced Collaboration and Sharing Capabilities
Mind maps created from webpages serve as excellent communication tools. Instead of sharing lengthy articles with team members or study partners, you can distribute a clean visual summary that highlights key points and their relationships. This ensures everyone starts with the same understanding of the source material.
The collaborative potential extends beyond simple sharing. Many mind mapping tools allow multiple people to edit the same map simultaneously, making them ideal for group research projects, team planning sessions, or classroom activities where everyone needs to engage with the same source materials.
Faster Review and Study Processes
When you need to revisit information weeks or months after initial exposure, scanning a well-organized mind map is dramatically faster than re-reading entire articles. The visual structure helps you quickly locate specific details while maintaining context of how they relate to the bigger picture.
This efficiency becomes particularly valuable during exam preparation, project reviews, or any situation where you need to refresh your understanding of multiple information sources. The time invested in creating initial mind maps pays dividends every time you need to access that information later.
Solution Landscape: Tools and Methods
The market offers various approaches for converting web content to mind maps, each with different strengths, limitations, and ideal use cases. Understanding this landscape helps you choose the right method for your specific needs and constraints.
Manual Methods and Traditional Software
Traditional mind mapping software requires you to manually extract content from webpages and reconstruct it within their interfaces. Tools like SimpleMind provide robust features for adding color, images, and organizing thoughts, but demand significant time investment for content transfer.
These manual approaches work well when you need highly customized maps or when working with simple webpages. However, they become increasingly impractical with complex or lengthy content, as the copying and pasting process can consume more time than the actual organization and analysis.
AI-Powered Solutions
AI tools represent the cutting edge of webpage-to-mind-map conversion. Services like AI website to mind map converters can transform webpage content into interactive mind maps instantly by entering any URL. These solutions use artificial intelligence to analyze content structure and automatically generate organized visual representations.
The emergence of AI mind map summarizers that instantly map out key points from webpages represents a significant advancement in efficiency. However, many AI solutions restrict editing capabilities or export options behind paywalls, limiting their practical utility for users who need to customize and share their maps.
ClipMind: The Integrated Approach
ClipMind bridges the gap between manual control and AI efficiency. As a free Chrome extension, it combines one-click webpage summarization with full editing capabilities and flexible export options. This unique combination addresses the core limitations of both traditional and AI-only approaches.
What sets ClipMind apart is its noise-filtering technology that removes ads, navigation elements, and irrelevant content before mind map generation. This ensures clean, focused visualizations that capture only the substantive content from webpages. The dual-view system accommodates both visual thinkers and text-oriented users within the same workflow.
Manual Method: Step-by-Step Guide
While AI tools offer impressive efficiency, understanding manual methods provides valuable insight into the mind mapping process and prepares you for situations where automated tools aren't available or appropriate.
Copy and Paste Content into Mind Mapping Software
Begin by selecting the relevant content from your target webpage. Be selective—copy only the substantive portions that contain the core information you need. Avoid including navigation elements, advertisements, or repetitive content that doesn't add value to your understanding.
Paste this content into your chosen mind mapping software. Many applications will create individual nodes for each paragraph or section, giving you raw material to work with. At this stage, don't worry about organization—focus on capturing the complete content you'll need for your map.
Organize Information Hierarchically
Review your pasted content and identify the main ideas, supporting points, and specific details. Create a central node that represents the webpage's primary topic, then build branches for major themes and sub-branches for supporting information.
This hierarchical organization is where the real thinking happens. As you move content into appropriate positions, you're actively processing the information and making decisions about relationships and importance. This engagement is what transforms passive reading into active learning.
Add Visual Elements and Connections
Enhance your mind map with visual elements that reinforce the content structure. Use different colors for various categories of information, add icons to highlight key points, and create connecting lines between related ideas that appear in different branches.
These visual cues do more than make your map attractive—they create additional memory triggers and help you see patterns in the information. The use of colors, shapes, and associations significantly enhances comprehension and recall.
Review and Refine the Structure
Step back from your nearly completed mind map and evaluate it as a whole. Check for balance—are some branches overcrowded while others are sparse? Look for missing connections between related concepts in different sections. Ensure the hierarchy accurately reflects the importance and relationships within the source content.
This review stage often reveals insights you missed during initial reading. The visual representation makes gaps in your understanding more apparent and highlights areas where you might need to revisit the original content for clarification.
AI-Powered Method with ClipMind
For most users, AI-powered tools like ClipMind offer the optimal balance of efficiency and control. The process eliminates tedious manual work while preserving your ability to customize and refine the results.
Install ClipMind Chrome Extension
The installation process follows standard Chrome extension procedures. Visit the Chrome Web Store, search for ClipMind, and click "Add to Chrome." Confirm the installation when prompted, and the extension will appear in your browser toolbar, ready for use.
The entire process takes less than a minute and requires no technical expertise. Unlike many AI tools, ClipMind doesn't require account creation or payment information, maintaining the privacy and simplicity that users appreciate.
Navigate to Target Webpage
Once installed, browse to any webpage you want to summarize. ClipMind works with most standard web content, including articles, blog posts, documentation, and research papers. The tool is particularly valuable with lengthy or complex content where manual summarization would be time-consuming.
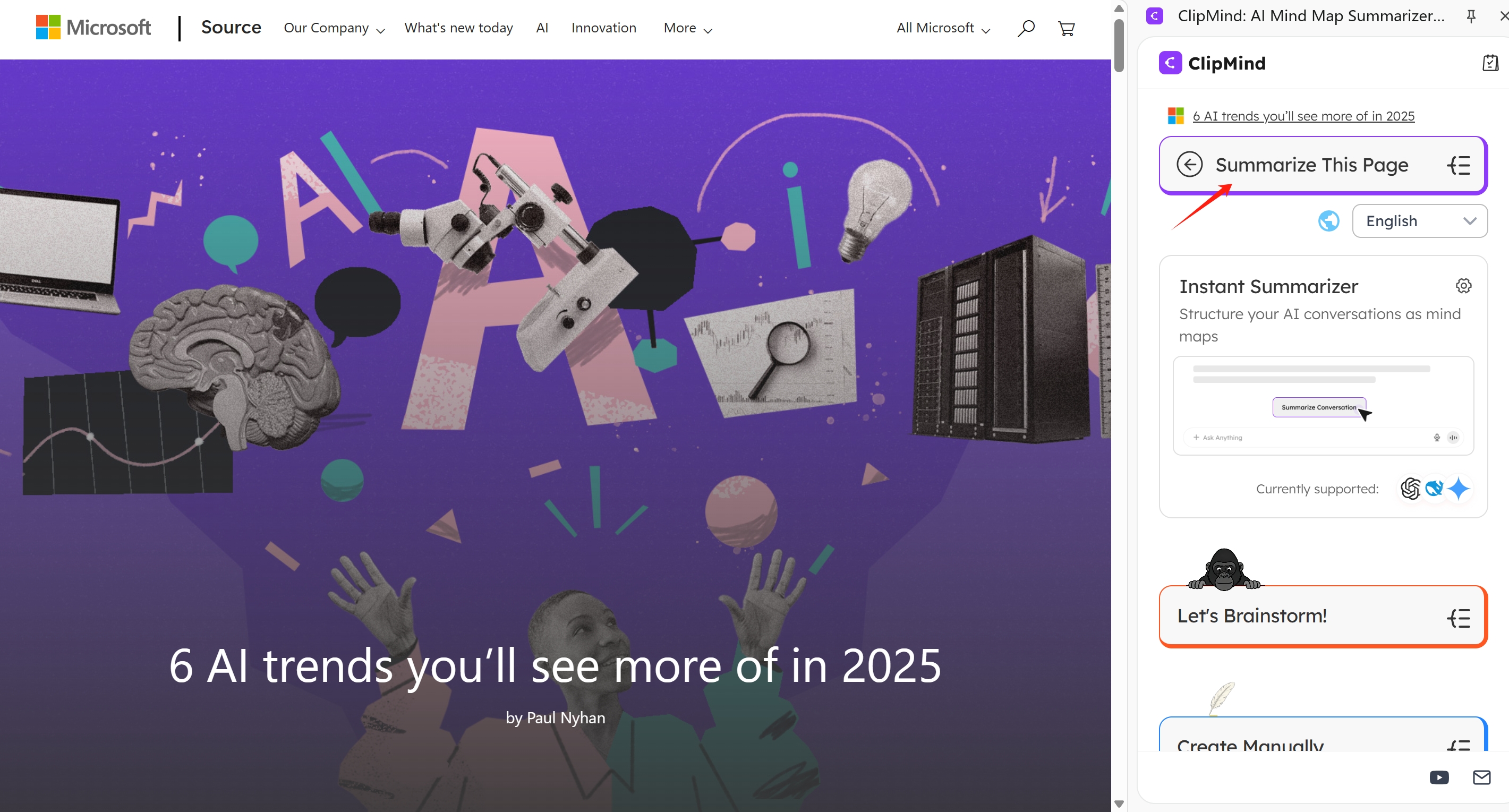
Click Summarize Button
With your target webpage loaded, click the ClipMind icon in your browser toolbar and select the summarize function. The AI immediately processes the page content, applying noise-filtering to remove ads, navigation elements, and other non-essential material.
This one-click operation eliminates what traditionally required 15-30 minutes of manual work. The speed doesn't compromise quality—ClipMind's algorithms are designed to identify and preserve the core substantive content while discarding distractions.
Review and Edit Generated Mind Map
ClipMind presents the summarized content in a clean, editable mind map interface. Unlike many AI tools that generate static images, ClipMind provides full editing capabilities, allowing you to modify nodes, rearrange structures, and add your own insights.
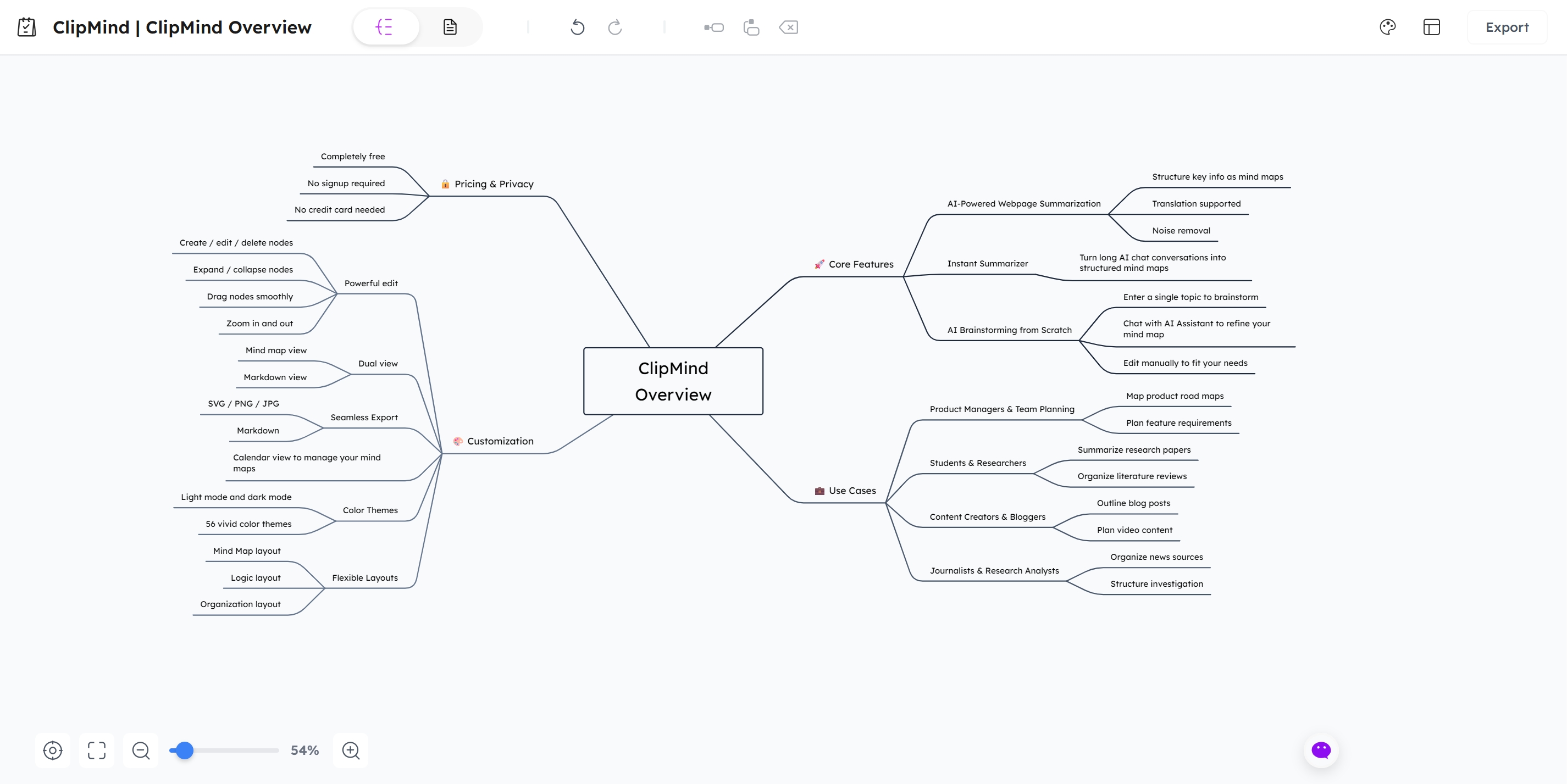
This editing flexibility mirrors the advantages mind maps have over traditional notes, allowing you to easily move ideas around and draw connections between different concepts. The ability to customize the AI-generated foundation ensures the final map truly reflects your understanding.
Export in Preferred Format
Once satisfied with your mind map, export it in your preferred format. ClipMind supports SVG for high-quality visuals and Markdown for text-based applications, with additional formats planned for future updates.
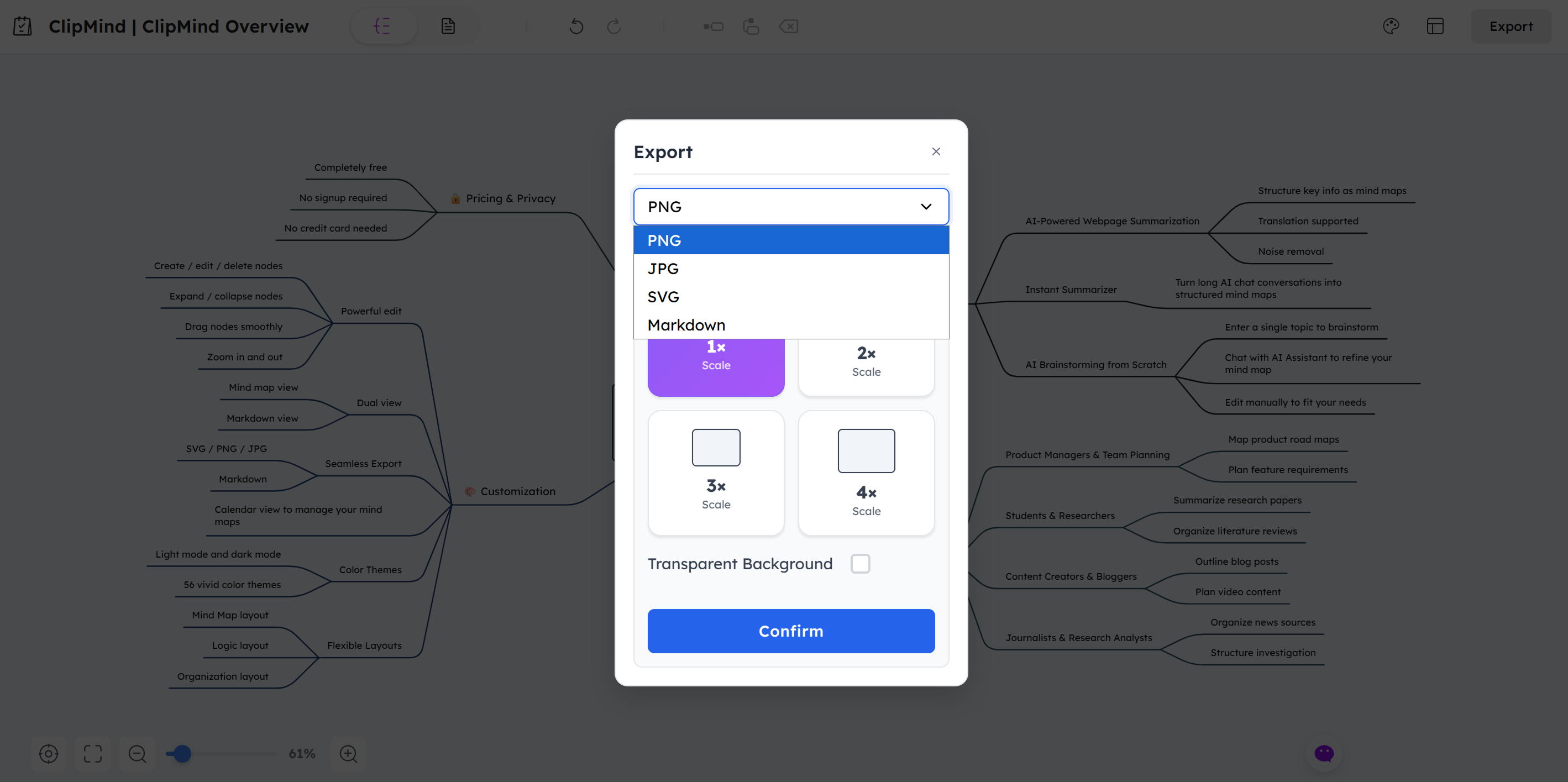
This export capability, offered completely free, addresses a significant limitation of many competing tools that restrict basic functionality behind paywalls. Whether you need to include mind maps in presentations, documents, or study materials, ClipMind ensures you have access to your work in usable formats.
Advanced ClipMind Features
Beyond basic summarization, ClipMind offers sophisticated features that enhance its utility across different use cases and user preferences. These advanced capabilities make it suitable for everything from quick reference maps to detailed knowledge organization systems.
Using Different Layouts
ClipMind provides three layout options that present the same information in different visual frameworks. The Mind Map layout uses traditional radial organization with a central topic and branching subtopics. The Logic Chart arranges information in a more structured, flowchart-like format that emphasizes sequential relationships. The Organization layout mimics corporate hierarchy charts, ideal for understanding authority structures or procedural workflows.
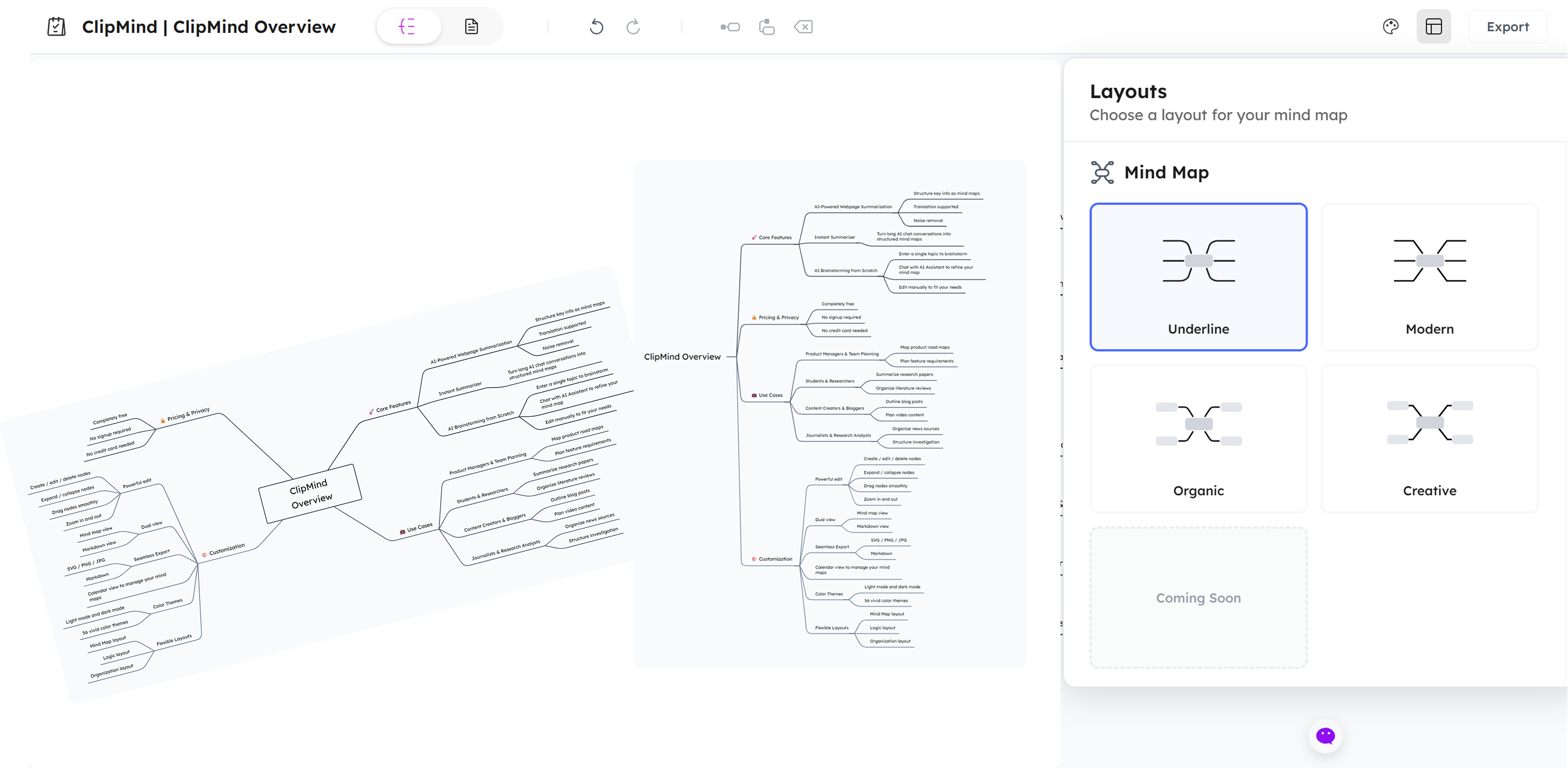
The ability to switch between layouts lets you view the same information through different conceptual lenses, often revealing patterns and relationships that weren't apparent in other formats. This flexibility makes ClipMind valuable for complex analysis where multiple perspectives enhance understanding.
Applying Themes for Visual Customization
Visual design significantly impacts how easily you can process and remember information. ClipMind offers eight color themes—Iris, Amethyst, Sunset, Ocean, Forest, Neon, Cherry Blossom, and Volcano—that apply consistent color coding across your mind map.
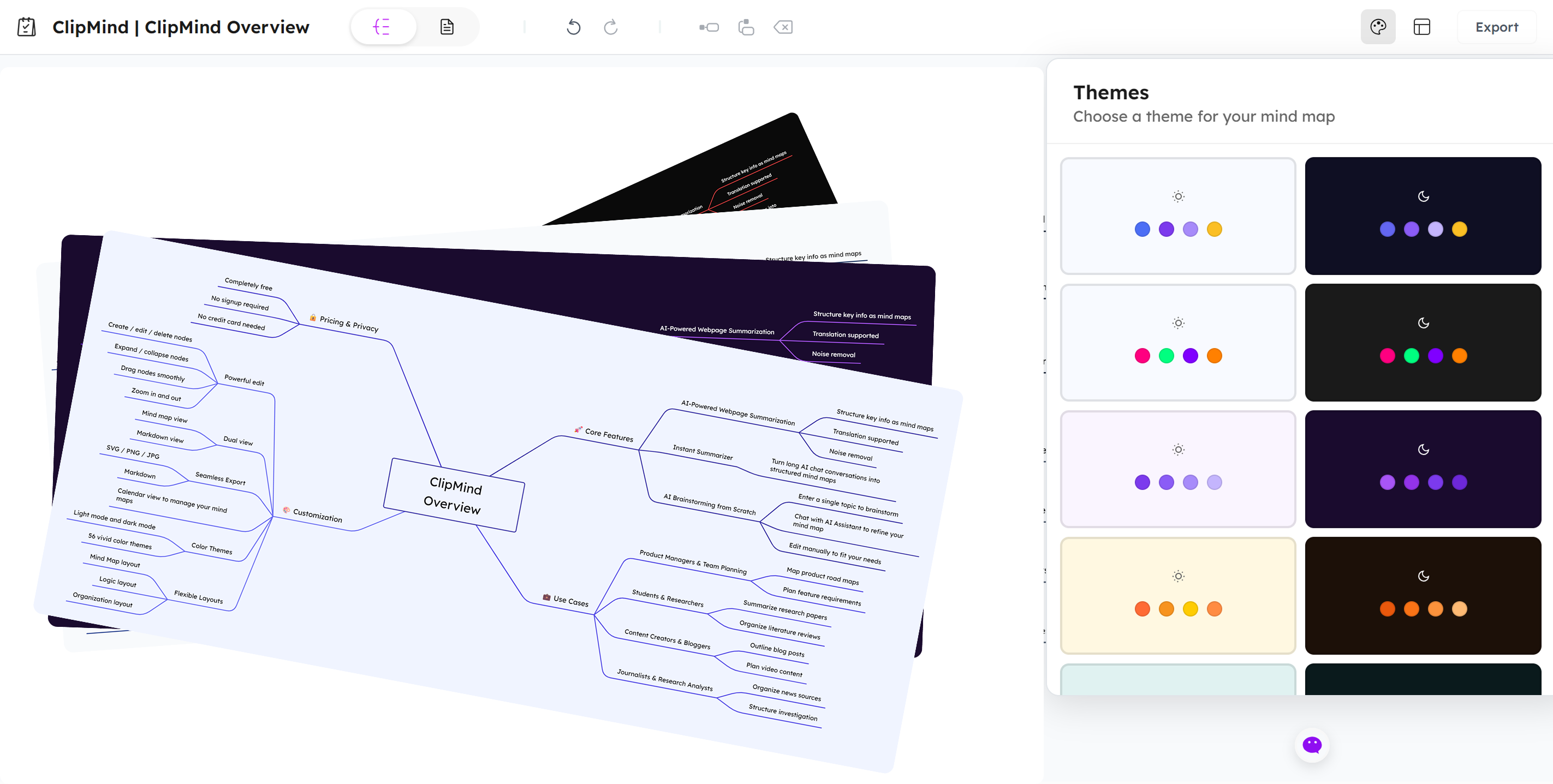
These themes do more than make your maps aesthetically pleasing. The strategic use of color helps categorize information, create visual hierarchy, and improve recall. Research on mind mapping effectiveness confirms that visual elements significantly enhance comprehension and memory.
Switching Between Map and Markdown Views
The dual-view system represents one of ClipMind's most innovative features. The Mind Map view provides the visual representation that makes relationships obvious at a glance. The Markdown view shows the same content in structured text format, ideal for detailed editing or when visual elements would be distracting.
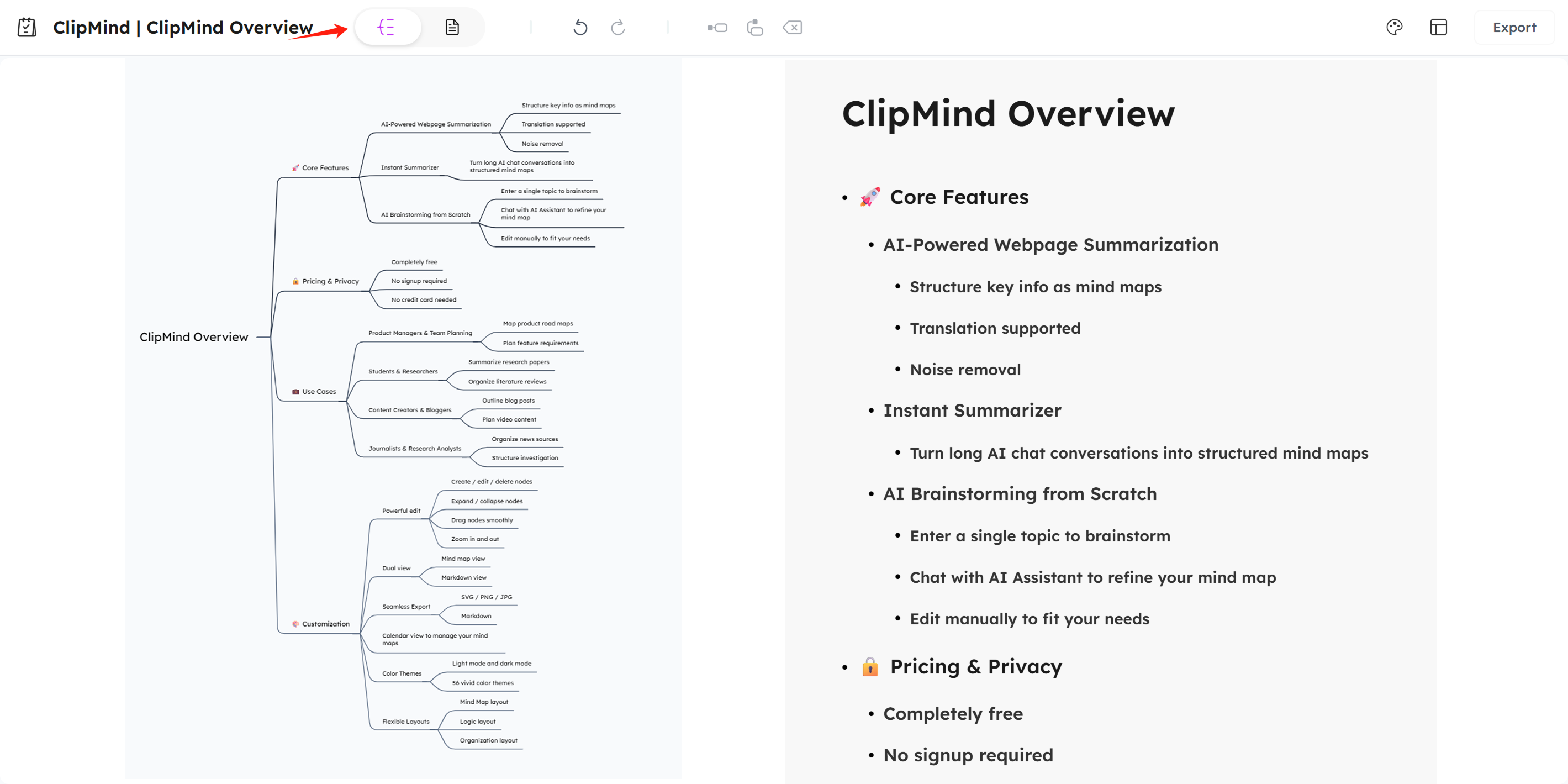
This flexibility accommodates different thinking styles and use cases. Visual thinkers can work primarily in the map view, while those who prefer textual organization can use the markdown interface. The seamless synchronization between views means you never lose work when switching perspectives.
Accessing History and Previous Maps
ClipMind maintains a history of your previous mind maps, allowing you to revisit and revise earlier work. This feature is particularly valuable for ongoing research projects, study programs, or any situation where you need to build knowledge incrementally across multiple sessions.
The history function transforms ClipMind from a simple summarization tool into a personal knowledge management system. By preserving your mapping work over time, it helps you track your learning journey and build upon previous understanding rather than starting from scratch each time.
Use Cases by Profession
The ability to convert webpages to mind maps delivers value across diverse professional contexts. Understanding how different roles can apply this technology helps you identify opportunities within your own work or studies.
Students Summarizing Research and Study Materials
Students face the constant challenge of processing large volumes of academic content from journal articles, textbook chapters, and online resources. Mind mapping these materials transforms passive reading into active learning, forcing engagement with the material's structure and relationships.

Research confirms that mind mapping improves reading comprehension by helping organize thoughts, allowing quick scanning, and promoting deeper understanding. For exam preparation, having key concepts visually mapped makes review sessions more efficient and effective.
Product Managers Mapping Requirements and Feedback
Product managers constantly synthesize information from multiple sources—user feedback, competitive analysis, technical documentation, and market research. Creating mind maps from these web-based resources helps identify patterns, prioritize features, and communicate product vision to development teams.
The visual nature of mind maps makes them ideal for stakeholder presentations where you need to show how different pieces of information connect to product decisions. The ability to quickly summarize lengthy documents ensures you capture all relevant considerations without getting bogged down in details.
Content Creators Outlining Articles and Planning Calendars
Content creators research extensively before writing, often consulting numerous web sources on a single topic. Converting these research materials into mind maps provides a structured outline for articles, videos, or social media content, ensuring comprehensive coverage while maintaining logical flow.
For content planning, mind maps help visualize relationships between different topics, identify content gaps, and maintain consistent messaging across multiple pieces. The efficiency of tools like ClipMind means creators can spend more time on original content and less on administrative organization.
Researchers Organizing Literature Reviews
Academic researchers must synthesize information from dozens or hundreds of sources when conducting literature reviews. Mind mapping these sources helps identify theoretical connections, methodological patterns, and knowledge gaps across the research landscape.
The visual organization makes it easier to see how different studies relate to each other and to your research questions. This big-picture perspective is difficult to achieve when working with linear notes or annotated bibliographies alone. The ability to export maps in multiple formats facilitates inclusion in research papers and presentations.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with advanced tools, you may encounter challenges when converting certain types of web content to mind maps. Understanding these potential issues and their solutions ensures successful outcomes across diverse source materials.
Handling Complex or Poorly Structured Webpages
Some webpages present challenges due to complex layouts, multiple content sections, or unconventional information architecture. When automated tools struggle with these pages, try focusing on specific content sections rather than attempting to map the entire page at once.
Most browsers allow you to select specific portions of a webpage before activating summarization tools. This targeted approach often yields better results than processing pages with mixed content types or complicated layouts. For particularly challenging pages, consider manual extraction of key sections followed by AI processing of the cleaned content.
Dealing with Paywalled or Restricted Content
Subscription-based content and password-protected materials present obvious challenges for automated tools. In these situations, focus on what you can access—abstracts, summaries, or publicly available portions—and use these as the foundation for your mind map.
Many academic databases provide structured abstracts that contain the essential information from full papers. These can serve as excellent starting points for mind maps, especially when combined with your own notes from any full-text access you might have through institutional subscriptions.
Managing Very Long Articles and Documents
Extremely lengthy content can produce overwhelming mind maps with too many nodes to be useful. When working with book-length web content or extensive reports, consider breaking the material into logical sections and creating separate maps for each.
Most mind mapping tools, including ClipMind, allow you to collapse branches, making it possible to work with detailed maps while maintaining a manageable visible structure. Start with high-level mapping to understand the overall architecture, then drill down into specific sections as needed.
Ensuring Accurate Content Extraction
Automated tools occasionally misinterpret content hierarchy or include irrelevant material. Always review AI-generated maps for accuracy, paying particular attention to the placement of main ideas versus supporting details.
The editing capabilities in tools like ClipMind make correction straightforward when the initial analysis misses the mark. Look for opportunities to simplify complex branches, combine related concepts, or reorganize information to better reflect the source content's intended meaning.
Best Practices for Effective Mind Maps
Creating useful mind maps involves more than simply transferring content from webpages to visual formats. These established practices ensure your maps serve as effective thinking tools rather than merely decorative representations.
Focus on Key Concepts and Main Ideas
The most common mistake in mind mapping is including too much detail. Effective maps prioritize keywords and associations over complete sentences, capturing the essence of ideas without reproducing entire paragraphs.
When converting web content, constantly ask yourself: "What is the core idea here?" and "How does this connect to other concepts?" This filtering process is where much of the learning value resides—the decisions about what to include and how to relate ideas deepen your engagement with the material.
Use Consistent Formatting and Color Coding
Develop a personal visual language for your mind maps and apply it consistently. Use specific colors for different types of information (blue for definitions, green for examples, red for important concepts), similar shapes for related ideas, and standardized line styles for different relationship types.
This consistency creates visual patterns that make your maps easier to interpret at a glance. When you return to a map weeks or months later, the formatting cues will help you quickly reorient yourself to the content structure and relationships.
Keep Branches Balanced and Organized
A well-structured mind map has relatively balanced branches with similar levels of detail. Avoid situations where one branch contains dozens of sub-points while others have only two or three. This imbalance often indicates incomplete thinking or poor content organization.
If you notice significant branch imbalance, reconsider whether you've correctly identified the main ideas or if some concepts should be combined or separated differently. The visual nature of mind maps makes these structural issues immediately apparent in ways that linear notes conceal.
Include Only Relevant Information
Resist the temptation to include interesting but tangential information that doesn't directly support your mapping purpose. Every additional node increases cognitive load and can obscure the core relationships you're trying to highlight.
This selective approach addresses the common challenge of too much content by forcing you to distinguish between essential and supplementary information. The discipline of exclusion is as valuable as the process of inclusion in creating effective mind maps.
Regularly Review and Update Maps
Mind maps are living documents that should evolve as your understanding deepens. Schedule regular reviews of important maps to incorporate new insights, correct misunderstandings, or add connections you initially missed.
This practice transforms static summaries into dynamic knowledge tools that grow with your learning. The flexibility of mind maps for editing makes them ideal for this iterative refinement process.
Comparison Table: Methods and Tools
Choosing the right approach for converting webpages to mind maps requires understanding the trade-offs between different methods. This comparison highlights key considerations to guide your selection process.
| Feature | Manual Methods | AI-Only Tools | ClipMind |
|---|---|---|---|
| Setup Time | Minutes | Minutes | Minutes |
| Processing Time | 15-45 minutes | Seconds | Seconds |
| Editing Capabilities | Full control | Often limited | Full control |
| Export Options | Varies by tool | Often restricted | Free SVG & Markdown |
| Noise Filtering | Manual | Varies | Automated |
| Learning Curve | Moderate | Low | Low |
| Cost | Freemium models | Subscription-based | Completely free |
| Ideal Use Case | Highly customized maps | Quick summaries | Balanced efficiency & control |
Side-by-Side Analysis
Manual methods offer maximum control but demand significant time investment, making them impractical for frequent use or lengthy content. Traditional mind mapping tools provide robust features but maintain the manual transfer bottleneck.
AI-only solutions deliver impressive speed but often restrict the editing and export capabilities that make mind maps truly useful. Many position these essential features as premium upgrades, reducing accessibility for students and individual users.
ClipMind's unique value proposition combines AI efficiency with manual control, addressing the core limitations of both approaches. The completely free model with full functionality makes advanced webpage summarization accessible to all users regardless of budget.
Time Investment and Learning Curve Considerations
When evaluating mind mapping software, consider both initial learning time and ongoing efficiency. Tools with steep learning curves may offer powerful features but prove impractical if you need quick results.
ClipMind's intuitive interface requires minimal learning while delivering professional-grade results. The one-click summarization eliminates the most time-consuming aspect of traditional mind mapping, while the editing tools ensure you maintain control over the final output.
Output Quality and Customization Options
The ultimate test of any mind mapping tool is the usefulness of its outputs. Manual methods can produce highly customized results but require artistic skill and design time. AI tools generate consistent but sometimes generic visualizations.
ClipMind strikes a balance with professionally designed templates that users can customize through editing, themes, and layouts. This approach delivers polished results without demanding design expertise, making quality mind mapping accessible to users with varying technical and artistic backgrounds.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
Converting webpages to mind maps transforms how we interact with digital information, moving from passive consumption to active organization and understanding. The techniques and tools covered in this guide provide multiple pathways to this more efficient approach, regardless of your technical comfort level or specific use case.
The most significant development in this space is the emergence of AI-powered tools like ClipMind that eliminate the manual labor previously required while preserving the editing control that makes mind maps personally meaningful. The combination of one-click summarization, noise-filtering technology, and completely free access represents a paradigm shift in how we can process web-based information.
Your next step should be experimentation. Start with a webpage you recently struggled to understand or remember, and apply either the manual method or ClipMind's AI approach. Compare the resulting mind map to your traditional notes and assess which better supports your comprehension and recall. The visual difference will likely surprise you, as will the efficiency gains once you incorporate these techniques into your regular workflow.
Learn More
- ClipMind Chrome Extension
- Advanced Mind Mapping Techniques
- Research on Visual Learning Effectiveness
- Content Management Strategies
- Productivity Tools Comparison
FAQs
-
How accurate is AI at summarizing webpages into mind maps? Modern AI achieves impressive accuracy in identifying main ideas and hierarchical relationships, though review and editing are still recommended. ClipMind's noise-filtering technology specifically targets irrelevant content like ads and navigation, improving focus on substantive material.
-
Can I use these methods on any website? Most standard content websites work well, though complex layouts or heavily interactive pages may present challenges. Paywalled content requires alternative approaches, such as working with available summaries or abstracts.
-
How long does it take to create a mind map from a webpage? Manual methods typically require 15-45 minutes depending on content length and complexity. AI tools like ClipMind can generate initial maps in seconds, with additional time for review and customization as needed.
-
Are there privacy concerns with AI summarization tools? ClipMind operates with strong privacy protections—no login required, no personal data collection, and your content stays on your device. Always review privacy policies for any tool you use, particularly those requiring account creation.
-
What's the best way to learn mind mapping? Start with simple, familiar content to practice identifying key concepts and relationships. Use templates or AI-generated maps as learning examples, then gradually develop your own style through experimentation and regular use.
-
Can multiple people collaborate on the same mind map? Many tools support real-time collaboration, though specific features vary. ClipMind focuses on individual use with export capabilities for sharing, while other platforms offer built-in multi-user editing.
-
How do I choose between manual and AI methods? Consider your available time, the importance of customization, and how frequently you'll use mind mapping. For regular use with various content types, AI tools like ClipMind offer the best balance of efficiency and control.
