What Is the Product Lifecycle? Stages and Strategies
Learn about the product lifecycle stages from development to decline, with practical strategies for product managers to optimize each phase effectively.
What Is the Product Lifecycle?
The product lifecycle is a fundamental framework that describes the journey of a product from its initial conception to its eventual retirement from the market. This concept helps product managers, marketers, and business leaders understand how products evolve over time and make informed decisions about resource allocation, marketing strategies, and product development priorities.
Understanding the product lifecycle is crucial because each stage presents unique challenges and opportunities. As products move through different phases, their market performance, customer adoption, and profitability patterns change significantly. The product lifecycle allows teams to anticipate these changes and develop appropriate strategies for each stage.
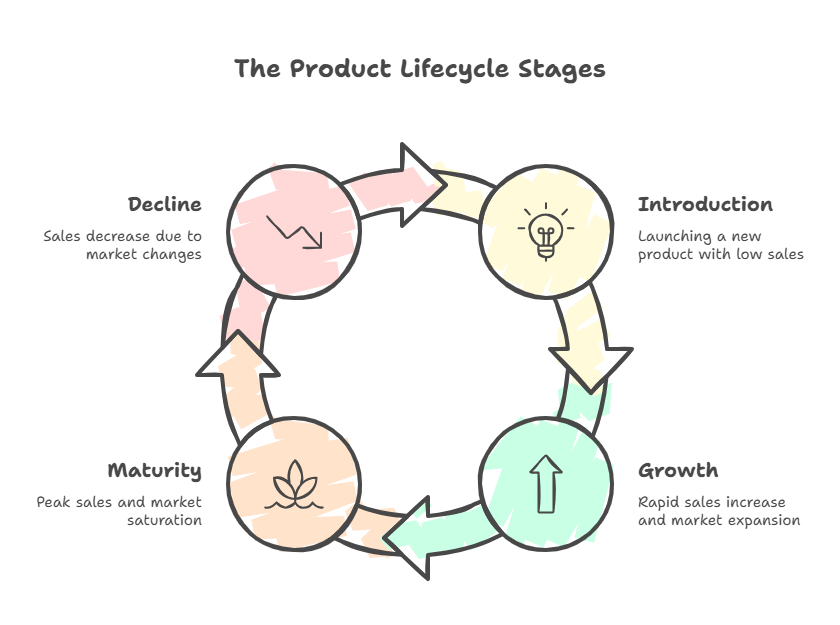
The Four Core Stages of the Product Lifecycle
Most experts recognize four primary stages in the product lifecycle, though some models include additional phases like saturation. According to Investopedia, these stages are introduction, growth, maturity, and decline.
Introduction Stage
The introduction stage begins when a product first enters the market. During this phase, sales are typically low as customers become aware of the new offering. Companies focus on building market awareness and educating potential customers about the product's benefits.
Key characteristics of the introduction stage include:
- High marketing and promotion costs
- Limited distribution channels
- Minimal competition
- Focus on early adopters
- Potential negative cash flow
Growth Stage
During the growth stage, product awareness increases and sales begin to accelerate rapidly. As Salesforce explains, marketing becomes slightly easier in this stage because customers are already familiar with your product.
Key growth stage indicators:
- Rapid sales increase
- Expanding market share
- Growing competition
- Improved profitability
- Product enhancements and variations
Maturity Stage
The maturity stage represents the peak of a product's market performance. According to Investopedia, this is typically the most profitable stage because production and marketing costs decline while sales stabilize.
Maturity stage characteristics:
- Market saturation
- Intense competition
- Price competition increases
- Focus on customer retention
- Product differentiation becomes crucial
Decline Stage
In the decline stage, sales begin to decrease as market demand diminishes. This can happen due to technological changes, shifting consumer preferences, or market saturation. Companies must decide whether to discontinue the product, sell it to another company, or find ways to extend its life.
Extended Product Lifecycle Models
Some frameworks expand the traditional four-stage model to include additional phases. The Aha.io product management guide describes a six-stage model that includes product development and saturation stages.
The development stage occurs before market introduction and involves research, design, and testing. The saturation phase, sometimes included between maturity and decline, occurs when market growth stagnates and competition becomes most intense.
Practical Applications for Product Teams
Understanding where your product sits in its lifecycle enables smarter strategic decisions. As Product School emphasizes, the product lifecycle is a fundamental concept that should guide product development and launch strategies throughout a product's existence.
Strategic Implications by Stage
- Introduction: Focus on market education and early adopter acquisition
- Growth: Scale operations and capture market share
- Maturity: Optimize operations and defend market position
- Decline: Decide on product retirement or revitalization strategies
Companies can push and pull investment in different areas, like marketing, sales, and research and development, based on the current stage of their product's lifecycle.
Visualizing Your Product Strategy
Mapping your product's position within its lifecycle helps align cross-functional teams and set realistic expectations. At ClipMind, we've found that creating visual representations of product lifecycles enables teams to better understand strategic priorities and resource allocation needs.
For product managers looking to apply these concepts, our AI Competitor Analyzer can help you understand where competing products sit in their lifecycles, while our Product Idea Brainstormer supports innovation during the development stage.
The product lifecycle framework provides a structured approach to managing products through their natural market evolution. By recognizing which stage your product is in, you can allocate resources more effectively, anticipate market changes, and develop strategies that maximize your product's potential throughout its entire journey.