What Is the MoSCoW Method? A Guide to Prioritization
Learn how the MoSCoW method helps teams prioritize requirements and tasks using four simple categories. Perfect for project managers and product teams.
What Is the MoSCoW Method?
The MoSCoW method is a prioritization technique used across software development, project management, and business analysis to help teams reach consensus on which requirements matter most. This framework creates a common understanding with stakeholders about the importance of delivering each requirement, feature, or task.
Originally developed as part of the DSDM Agile project delivery framework, MoSCoW has become widely adopted in agile software development approaches like Scrum and rapid application development. The method's strength lies in its simplicity—it categorizes work into four clear priority levels that help teams focus on what truly matters.
Understanding the Four MoSCoW Categories
The acronym MoSCoW represents four priority categories that help teams separate critical tasks from less essential ones. Each category serves a distinct purpose in the prioritization process.
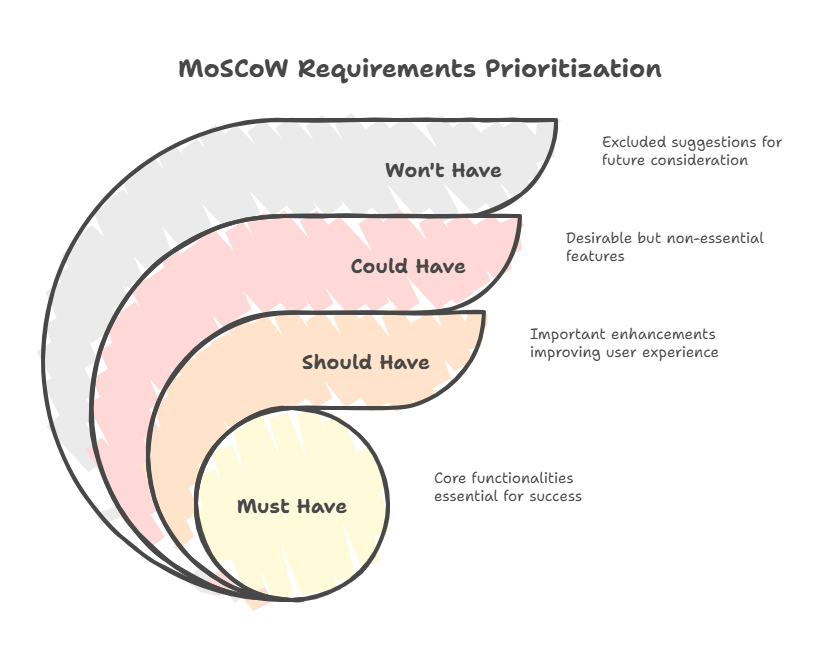
Must Have
Must Have requirements are non-negotiable—they represent the absolute minimum for project success. Without these elements, the project would be considered a failure. These are the core functionalities that deliver the fundamental value proposition.
Think of Must Haves as the foundation of your project. In software development, this might include basic user authentication or core transaction processing. According to prioritization experts, these requirements typically receive the majority of your efforts and resources because they make the greatest impact on your end goal.
Should Have
Should Have requirements are important but not critical. They add significant value and should be included if possible, but the project could still succeed without them. These items often represent enhancements that improve user experience or efficiency.
Unlike Must Haves, Should Haves can be delayed if necessary, though their absence might cause some inconvenience or reduced functionality. They're the features that stakeholders really want but could live without in a pinch.
Could Have
Could Have requirements are desirable but not necessary. These are the nice-to-have elements that would enhance the product or project but won't impact core functionality if omitted. They typically represent low-priority items that can be easily postponed.
Could Haves are often the first to be cut when timelines tighten or resources shrink. They provide flexibility in planning while ensuring that valuable but non-essential ideas aren't completely forgotten.
Won't Have
Won't Have requirements are explicitly excluded from the current project scope. This category serves an important psychological function—it acknowledges stakeholder suggestions while clearly communicating they won't be implemented now.
By creating space for Won't Haves, the MoSCoW method helps manage expectations and prevents scope creep. These items might be considered for future releases but are definitively off the table for the current iteration.
How to Implement the MoSCoW Method
Implementing the MoSCoW method follows a straightforward process that teams can adapt to their specific needs and workflows.
Step 1: List All Requirements
Begin by gathering all potential requirements, features, or tasks. This comprehensive list should include everything stakeholders have requested or team members have identified. Use brainstorming sessions, stakeholder interviews, or existing documentation to ensure nothing important is missed.
Step 2: Categorize Each Item
Work with your team and stakeholders to assign each requirement to one of the four MoSCoW categories. This collaborative process helps build consensus and ensures everyone understands the prioritization rationale. The MoSCoW method works by dedicating resources to priorities that will make the best impact on your end goal.
Step 3: Validate and Refine
Review your categorized list to ensure it's realistic given your constraints. A common pitfall is having too many Must Haves—if everything is critical, nothing truly is. Use this step to make tough decisions and adjust categories as needed.
Step 4: Execute and Revisit
Use your prioritized list to guide development and decision-making. The MoSCoW method is particularly effective when used with timeboxing approaches where deadlines are fixed, forcing focus on the most important requirements.
Benefits of Using MoSCoW Prioritization
The MoSCoW method offers several advantages that make it popular among project teams and product managers.
- Clear communication - The simple categories make it easy for everyone to understand what's important
- Stakeholder alignment - The collaborative categorization process builds consensus and manages expectations
- Scope management - Explicit Won't Have category helps prevent scope creep
- Flexible planning - The framework accommodates changing priorities while maintaining focus
- Resource optimization - Helps teams allocate limited resources to highest-impact work
Common Challenges and Solutions
While powerful, the MoSCoW method isn't without its challenges. Teams often struggle with category inflation—where too many items end up as Must Haves. To counter this, establish clear criteria for each category and be willing to make tough trade-off decisions.
Another common issue is stakeholder disagreement about categorization. Facilitate open discussions where team members can explain their reasoning and reach compromise. Remember that the method is designed to help you prioritize tasks, projects, and goals more effectively through structured conversation.
MoSCoW in Agile and Beyond
The MoSCoW method fits naturally within agile frameworks where prioritization is continuous. Teams can use it during sprint planning to select which user stories to include, or during product backlog refinement to keep the backlog organized and focused.
Beyond software development, the framework has proven valuable in marketing campaigns, research projects, event planning, and personal productivity. Any situation involving limited resources and multiple competing priorities can benefit from MoSCoW's structured approach to decision-making.
Getting Started with MoSCoW
Ready to implement the MoSCoW method in your projects? Start with a small, well-defined initiative to build confidence. Gather your team, list your requirements, and begin the categorization process. The framework's simplicity means you can start seeing benefits almost immediately.
For teams looking to streamline their MoSCoW implementation, consider using ClipMind's MoSCoW Analyzer to organize and visualize your priorities. The tool helps you create clear mind maps of your categorized requirements, making it easier to communicate priorities and track decisions across your organization.
The MoSCoW method's enduring popularity stems from its elegant simplicity and practical effectiveness. By providing a clear framework for separating the essential from the desirable, it helps teams deliver maximum value with limited resources—exactly what modern projects demand.