How to Create Empathy Maps for Better UX Design
Learn how to create effective empathy maps to understand user needs, align your team, and design better user experiences with this practical guide.
What Are Empathy Maps and Why They Matter
Empathy maps are collaborative visualization tools that help UX teams understand and align on user perspectives. By mapping what users think, feel, say, and do, these diagrams create a shared understanding of user needs that drives better design decisions.
Empathy mapping keeps features tuned to the desires of your users and helps you avoid the hefty cost of pursuing the wrong projects by getting the product right the first time. Unlike user personas or journey maps, empathy maps focus specifically on capturing user attitudes and behaviors in a simple, digestible format that teams can quickly reference throughout the design process.
The Four Quadrants of an Empathy Map
Traditional empathy maps are divided into four key quadrants that capture different aspects of the user experience. Understanding each section helps create a comprehensive picture of your user's world.
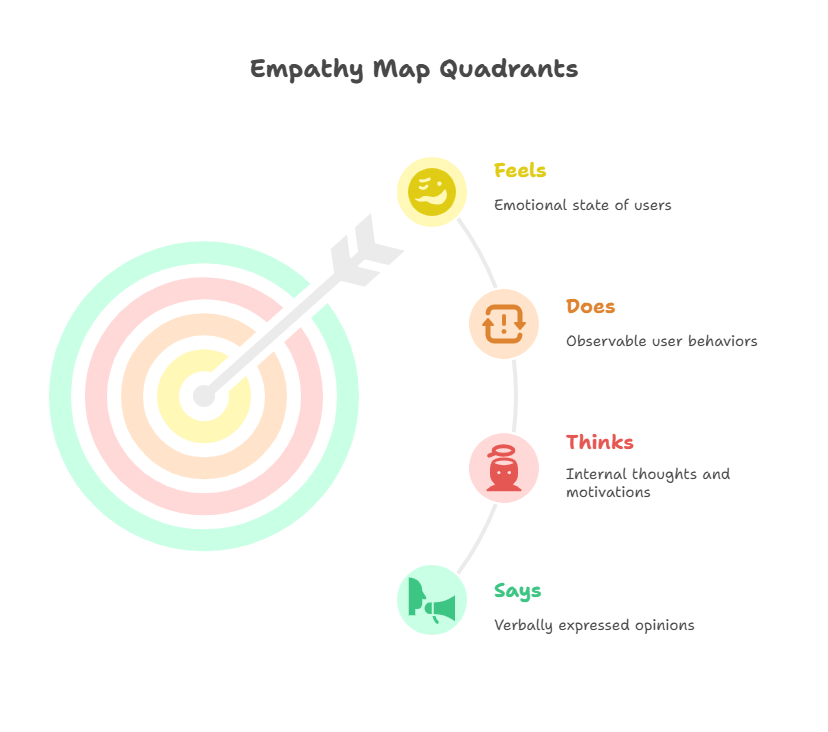
Says
This quadrant captures what users verbally express during research sessions. Include direct quotes from interviews, surveys, or usability tests. For example, a user might say "I get frustrated when I can't find the search function quickly" or "This feature saves me so much time." These statements provide concrete evidence of user preferences and pain points.
Thinks
The thinks quadrant explores what users might not say aloud but likely consider during their experience. This includes internal thoughts, concerns, and motivations that influence their behavior. Users might think "Is this secure enough for my data?" or "I hope this doesn't take too long to figure out." Capturing these unspoken thoughts reveals deeper user needs.
Does
This section documents observable user behaviors and actions. Note what users actually do when interacting with your product, including workarounds they develop or patterns you observe. Examples include "Refreshes the page multiple times" or "Uses keyboard shortcuts instead of clicking buttons." These behaviors often contradict what users say, providing valuable insights.
Feels
The feels quadrant captures the emotional state of users throughout their experience. Identify emotions like frustration, confusion, satisfaction, or delight. Users might feel anxious about making mistakes, excited when they accomplish a task quickly, or relieved when they find what they need. Understanding emotional responses helps design for better user experiences.
How to Create Effective Empathy Maps
Creating impactful empathy maps requires careful planning and execution. Follow this step-by-step process to ensure your maps provide genuine value to your design process.
Gather User Research Data
Start by collecting and reviewing user research before your mapping session. Empathy maps work best when created collaboratively, so schedule a meeting with your project team and ask them to review user research data in advance. Use data from interviews, surveys, usability tests, and analytics to ensure your map reflects real user behaviors rather than assumptions.
Conduct Collaborative Mapping Sessions
Bring your team together for a structured mapping session using physical or digital tools. Visualizing user attitudes and behaviors in an empathy map helps UX teams align on a deep understanding of end users. Begin with a 1:1 mapping approach—one user or persona per empathy map—to maintain focus and clarity. Encourage team members to contribute observations from their different perspectives.
Analyze and Synthesize Insights
Once you've populated all four quadrants, look for patterns, contradictions, and surprises. Notice when what users say differs from what they do, or when their thoughts conflict with their feelings. These inconsistencies often reveal the most valuable insights for design improvements. Use these findings to identify user needs and pain points that should inform your design decisions.
Integrating Empathy Maps into Your UX Process
Empathy maps deliver the most value when they become living documents that evolve with your understanding of users. Here's how to make them an integral part of your design workflow.
Use Throughout the Design Process
Empathy maps should be used throughout any UX process to establish common ground among team members and to understand and prioritize user needs. Refer to them during ideation sessions to ensure concepts address real user problems. Use them during design critiques to evaluate whether solutions align with user perspectives. Update them as you gather new research insights.
Connect to Other UX Tools
Empathy maps work best when combined with other UX methodologies. They can serve as a first step in the creation of personas by synthesizing themes across user groups. Use them alongside journey maps to understand both the emotional and practical aspects of user experiences. They also provide valuable context for usability testing by highlighting areas where users might struggle emotionally or cognitively.
Best Practices for Empathy Mapping Success
Follow these guidelines to ensure your empathy maps provide accurate, actionable insights that improve your design outcomes.
Focus on Specific Contexts
Create empathy maps for specific scenarios or tasks rather than trying to capture a user's entire experience. A map focused on "first-time setup" will yield different insights than one focused on "advanced feature usage." This specificity makes your maps more actionable and relevant to particular design challenges.
Validate with Real Data
Base your empathy maps on actual user research rather than assumptions or stereotypes. The goal of a UX designer is to create frictionless, user-friendly designs for your users, and this requires genuine empathy built on real observations. When you make claims about what users think or feel, ensure you can point to research data that supports these insights.
Keep Them Accessible and Evolving
Display your empathy maps where team members can easily reference them, and update them regularly as you learn more about your users. Your empathy map can change and evolve along with your users' needs, so treat them as living documents rather than one-time exercises. Regular reviews ensure your team maintains a current understanding of user perspectives.
Streamline Your Empathy Mapping with ClipMind
Creating and maintaining empathy maps can be time-consuming, but the right tools can simplify the process. ClipMind offers powerful visualization features that make empathy mapping more efficient and collaborative.
Our platform helps teams capture and organize user insights into structured empathy maps that can be easily shared and updated. The AI Outline Maker can help you structure your mapping sessions, while our visual workspace ensures everyone stays aligned on user understanding throughout the design process.
Whether you're working remotely or in-person, ClipMind provides the flexibility to create empathy maps that genuinely reflect your users' experiences and drive better design decisions.