TL; DR
- Starbursting shifts teams from solution-jumping to comprehensive questioning using Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How frameworks
- AI-powered tools like ClipMind can automatically generate relevant questions and suggest follow-ups, saving significant setup time
- The method helps product teams uncover hidden assumptions, identify knowledge gaps, and create more robust product requirements
- Digital starbursting enables real-time collaboration and seamless conversion of questions into actionable documentation
- Combining visual mind maps with structured Markdown views bridges creative exploration with practical implementation
Introduction
I've watched countless product teams rush from initial ideas to solutions without asking the right questions first. The excitement of a new concept often leads to premature development, only to discover critical gaps in understanding user needs, technical constraints, or market viability later. This pattern of solution-jumping costs teams time, resources, and sometimes entire product initiatives.
Starbursting brainstorming offers a systematic approach to prevent these costly mistakes by forcing teams to focus entirely on questions before answers. As research from Product School indicates, product development teams specifically struggle with balancing market viability and avoiding premature solution jumping. Starbursting addresses these challenges directly through structured questioning.
What makes modern starbursting particularly powerful is how AI-enhanced tools like ClipMind can accelerate the process while maintaining the method's rigorous framework. Instead of starting with blank whiteboards, teams can now generate comprehensive question frameworks automatically and collaborate in real-time, whether working remotely or in-person.
What is Starbursting Brainstorming?
Starbursting is a question-focused brainstorming technique that uses a star-shaped diagram to organize questions around a central topic. Unlike traditional brainstorming that generates answers and solutions, starbursting deliberately postpones solution development to ensure comprehensive exploration of all aspects of an idea.
The method employs a six-point framework representing the fundamental question categories: Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How. Each point of the star becomes a category for generating relevant questions, creating a systematic approach to idea exploration. As MasterClass explains, starbursting is primarily used for decision-making when teams need to narrow down several options to the best choice.
The technique has evolved from broader brainstorming methods originally developed by Alex Osborn in 1941 as creative problem-solving approaches. While traditional brainstorming often suffers from groupthink and disengaged participants, starbursting's structured framework keeps teams focused and ensures diverse perspectives are captured through systematic questioning.
Why Starbursting Matters for Product Development
Product development represents one of the most valuable applications for starbursting because it directly addresses common pitfalls that derail product initiatives. When teams jump straight to solutions, they often miss critical considerations around user experience, technical feasibility, market timing, and resource requirements.
Starbursting prevents premature solution development by forcing teams to thoroughly examine an idea from all angles. This systematic questioning approach helps identify assumptions, uncover knowledge gaps, and surface potential challenges early in the process. According to Fictiv's research on product concept generation, systematic idea generation enables designers to enter prototyping phases more effectively.
The method also democratizes the brainstorming process by providing a clear structure that helps quieter team members contribute valuable questions. This addresses the common brainstorming challenges of groupthink, personality differences, and disengaged participants that plague traditional brainstorming sessions.
Perhaps most importantly, starbursting creates a comprehensive foundation for product requirements. By generating questions across all six categories, teams ensure they've considered user perspectives, feature specifications, timing considerations, implementation details, business rationale, and contextual factors before committing development resources.
Traditional vs Modern Starbursting Approaches
The core principles of starbursting remain consistent across implementation methods, but how teams execute the technique has evolved significantly with digital tools and AI enhancements.
Traditional manual starbursting typically involves physical whiteboards, sticky notes, and marker pens. Teams gather in conference rooms, write the central topic in the middle of the board, and draw a six-point star around it. Participants then write questions on sticky notes and place them under the appropriate categories. While this approach has the benefit of physical presence and tactile engagement, it suffers from limitations in remote collaboration, documentation, and organization.
Digital starbursting tools like Mural and Figma enable remote teams to collaborate in real-time using virtual whiteboards. These platforms overcome geographical barriers and provide better organization capabilities, but still require manual question generation and categorization.
AI-enhanced starbursting with tools like ClipMind represents the modern evolution of the technique. These platforms combine the visual structure of starbursting with AI capabilities that can automatically generate relevant questions, suggest follow-up inquiries, and help organize questions by priority and theme.
| Aspect | Manual Whiteboards | Digital Tools | AI-Powered Platforms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Setup Time | 10-15 minutes | 5-10 minutes | 1-2 minutes |
| Remote Collaboration | Limited | Excellent | Excellent |
| Question Generation | Manual | Manual | AI-assisted |
| Organization | Basic | Good | Advanced |
| Documentation | Manual photos/notes | Automatic saving | Multiple export formats |
| Follow-up Suggestions | None | Limited | AI-powered |
ClipMind's unique approach bridges the gap between creative exploration and practical implementation through its dual-view interface. Teams can work visually in mind map mode during brainstorming sessions, then instantly switch to Markdown view to organize questions into structured documentation.
Step-by-Step Guide to Starbursting with ClipMind
Implementing starbursting with ClipMind transforms what was once a manual, time-intensive process into an efficient, AI-enhanced workflow. The platform's specific features align perfectly with starbursting's structured approach while adding intelligent assistance that improves question quality and coverage.
Setting Up Your Central Topic
The foundation of any successful starbursting session begins with a well-defined central topic. This isn't just a broad subject area—it should be a specific idea, problem statement, or product concept that your team needs to explore. According to EasyRetro's starbursting guide, teams start with an idea, question, or challenge at the center and create a six-point star around it.
In ClipMind, you begin by creating a new mind map and placing your central topic in the center node. The AI Brainstorm feature can help refine your topic if you're starting with a vague concept. For example, instead of "new mobile app," you might refine to "fitness tracking app for senior citizens with limited smartphone experience."
Effective central topics share several characteristics:
- Specificity: Narrow enough to generate focused questions
- Relevance: Aligned with current business priorities and user needs
- Exploratory: Open to multiple perspectives and questioning angles
- Actionable: Likely to lead to concrete next steps or decisions
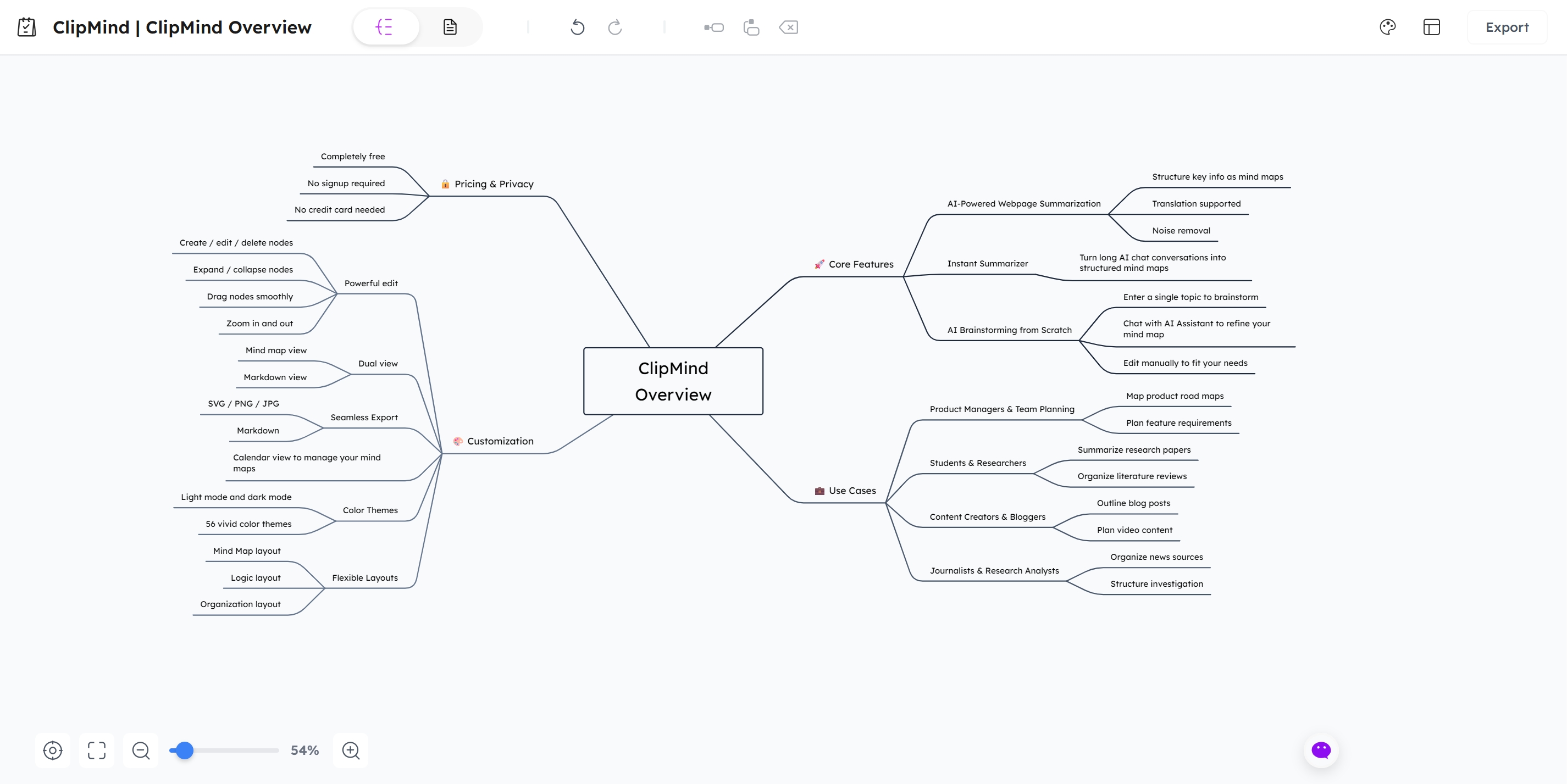
Building the Six-Point Question Framework
Once your central topic is established, ClipMind's AI Brainstorm feature can automatically generate the initial six-point starbursting framework. The AI understands the starbursting methodology and will create relevant question categories and starter questions for each point of the star.
Who Questions focus on the people involved—users, stakeholders, team members, and affected parties. For a product development context, this might include: "Who are our primary target users?" "Who will be responsible for implementation?" "Who might be negatively impacted by this product?"
What Questions explore the features, functionalities, and deliverables. Examples include: "What core problems does this solve?" "What features are essential for launch?" "What technical constraints might we face?"
When Questions address timing, sequencing, and deadlines. Relevant questions might be: "When should we launch to maximize market impact?" "When will key resources become available?" "When should we conduct user testing?"
Where Questions consider location, distribution, and context. These could include: "Where will users primarily access this product?" "Where should we focus our marketing efforts?" "Where might implementation challenges arise?"
Why Questions examine purpose, justification, and business rationale. Important questions include: "Why would users choose this over alternatives?" "Why is this aligned with our company strategy?" "Why now rather than later?"
How Questions focus on implementation, processes, and methods. These might be: "How will we measure success?" "How does this integrate with existing systems?" "How will we handle scalability?"
According to Project Bliss, the technique uses this six-pointed star with categories like 'Who', 'What', 'When', 'Where', 'Why', and 'How' to generate comprehensive questioning. ClipMind's AI enhances this by suggesting additional relevant questions for each category based on your specific central topic.
Generating and Organizing Questions
With the framework established, your team can begin generating questions for each category. ClipMind's collaborative features allow multiple team members to contribute questions simultaneously, whether they're in the same room or working remotely across time zones.
The key principle during this phase is quantity over quality—generate as many questions as possible without filtering or evaluating them initially. As Figma's starbursting template guidance suggests, teams should generate as many questions as possible for each of the leading phrases without worrying about answers initially.
ClipMind's AI Assistant can suggest follow-up questions based on the team's inputs, helping to deepen the exploration and ensure comprehensive coverage. For example, if someone adds "Who are our primary users?" the AI might suggest "Who are our secondary users?" or "Who are the decision-makers versus end-users?"
Once question generation is complete, the organization phase begins. ClipMind enables several organization strategies:
- Priority tagging: Mark questions as high, medium, or low priority
- Theme grouping: Cluster related questions together within categories
- Dependency mapping: Identify questions that need to be answered before others
- Ownership assignment: Designate team members responsible for answering specific questions
This organization transforms a collection of questions into a structured action plan for further research and decision-making.
Implementing Starbursting in Team Meetings
Facilitating effective starbursting sessions requires careful planning and execution, whether your team is co-located or distributed. The structure provided by ClipMind helps maintain focus and productivity throughout the session.
For in-person meetings, project ClipMind on a large screen and have team members contribute questions using their own devices or through a designated facilitator. For remote teams, share your screen and use ClipMind's real-time collaboration features to allow simultaneous editing.
According to HSI's remote collaboration research, remote teams benefit from foundational tools and guidance, including different meeting styles. Starbursting sessions work particularly well as dedicated workshops rather than trying to squeeze them into regular status meetings.
Time management is crucial for productive starbursting. Lucid's starbursting guide recommends setting time limits to manage the infinite number of possible questions. A typical session might allocate:
- 5 minutes for topic refinement and framework setup
- 20-30 minutes for question generation across all six categories
- 10-15 minutes for question organization and prioritization
- 5 minutes for assigning next steps and follow-up actions
Asynchronous starbursting represents another powerful approach using ClipMind. Instead of requiring everyone to meet simultaneously, you can create the central topic and framework, then share the mind map with your team to contribute questions over a defined period (e.g., 24-48 hours). This approach accommodates different working styles and time zones while still generating comprehensive question sets.
From Questions to Actionable Insights
The true value of starbursting emerges when teams systematically convert questions into answers and those answers into product decisions. This transition from exploration to action represents the most critical phase of the process.
Mural's starbursting approach suggests breaking brainstorming into two sessions: one for starbursting to find questions and another for answering questions via structured brainstorming. ClipMind supports this two-phase approach through its export and documentation features.
After your starbursting session, use ClipMind's export functionality to convert your question map into a Markdown document. This creates a structured question inventory that can be integrated into product requirements documents, research plans, or decision frameworks.
Pattern identification becomes easier when you review the complete question set. Look for:
- Knowledge gaps: Questions that no one can answer immediately, indicating areas needing research
- Assumption clusters: Multiple questions based on unverified assumptions
- Priority themes: Questions that repeatedly touch on critical success factors
- Stakeholder concerns: Questions highlighting different perspectives and interests
Answer development should follow a systematic approach. Assign question clusters to relevant team members based on expertise and responsibility. Set deadlines for providing answers and document the responses directly in ClipMind or your preferred project management tool.
The final step involves synthesis and decision-making. Review the answered questions to identify implications for your product strategy, feature priorities, implementation approach, and success metrics. This comprehensive understanding enables more informed decisions and reduces the risk of overlooking critical factors.
Advanced Starbursting Techniques
Once your team masters basic starbursting, several advanced techniques can enhance the method's effectiveness for complex product challenges.
Layered starbursting involves using the answers from your initial questions as central topics for subsequent starbursting sessions. For example, if your initial session generated the question "How will users onboard to our product?" and the answer revealed specific complexity, you might conduct a focused starbursting session specifically on "user onboarding flow."
Cross-category questioning encourages teams to explore connections between different question categories. For instance, how do "Who" considerations (user characteristics) influence "How" questions (implementation approach)? ClipMind's visual interface makes these connections visible through relationship lines and grouping features.
Combination methods integrate starbursting with other brainstorming techniques. For example, you might use starbursting for initial exploration, followed by SWOT analysis to evaluate the insights, then priority mapping to determine implementation sequence. MindManager's starbursting guide notes that expert facilitators use starbursting to brainstorm and explore different product dimensions including target audience, features, user experience, distribution channels, and marketing strategies.
AI-enhanced gap analysis uses ClipMind's AI Assistant to identify potential question gaps after the initial generation phase. The AI can analyze your question set and suggest additional areas for exploration based on common patterns in product development or specific knowledge about your industry.
Measuring Starbursting Effectiveness
Like any business process, starbursting should be evaluated for its impact on product outcomes and team effectiveness. Establishing clear metrics helps refine your approach and demonstrate the method's value to stakeholders.

Process metrics focus on the starbursting sessions themselves:
- Question coverage: Percentage of six categories thoroughly explored
- Participation rate: Number of team members contributing questions
- Time efficiency: Reduction in session duration with practice and tooling
- Question-to-answer ratio: Percentage of generated questions that receive substantive answers
Outcome metrics measure starbursting's impact on product development:
- Requirement completeness: Reduction in late-added requirements during development
- Assumption validation: Percentage of initial assumptions that proved accurate
- Decision confidence: Team confidence levels in product decisions post-starbursting
- Stakeholder alignment: Reduction in conflicting perspectives or requirements
According to performance measurement research, performance metrics serve as indicators that businesses use to gauge the performance of various organizational elements. For starbursting, the most valuable metrics are those that connect the questioning process to tangible product outcomes.
Continuous improvement of your starbursting practice involves regularly reviewing these metrics and adjusting your approach. This might include refining how you define central topics, adjusting time allocations for different phases, or improving how you convert questions into actionable insights.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Even with a structured method like starbursting, teams can encounter challenges that reduce effectiveness. Recognizing these common pitfalls helps you prevent them or address them quickly when they occur.
Solution contamination happens when team members slip into answer mode during question generation. This often manifests as questions that imply solutions, such as "How can we implement a gamification system?" rather than "How might we increase user engagement?" ClipMind's AI can help detect these solution-oriented questions and suggest more open alternatives.
Category imbalance occurs when teams focus disproportionately on certain question types while neglecting others. Many product teams naturally gravitate toward "What" and "How" questions while under-exploring "Who" and "Why" considerations. The visual balance in ClipMind's star diagram makes category imbalance immediately apparent, allowing facilitators to redirect attention to neglected areas.
Question surface-level when teams don't dig deep enough into each category. The first questions that come to mind are often obvious and high-level. LinkedIn's starbursting advice emphasizes that teams should focus on asking the right questions to uncover idea potential and avoid pitfalls that may hinder success. ClipMind's AI Assistant suggests follow-up questions that probe deeper into each area.
Documentation breakdown happens when the valuable questions and insights generated during starbursting aren't properly captured and integrated into product development workflows. ClipMind's export features and Markdown view help bridge this gap by making it easy to transfer starbursting outputs into product requirements, research plans, and decision documentation.
Conclusion
Starbursting brainstorming represents a powerful shift from solution-oriented thinking to comprehensive questioning—a approach particularly valuable in product development where unexamined assumptions can lead to costly mistakes. The structured framework of Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How ensures teams explore ideas from all relevant perspectives before committing to development paths.
Modern AI-enhanced tools like ClipMind transform starbursting from a manual, time-intensive process into an efficient, collaborative practice. The ability to automatically generate relevant questions, collaborate in real-time regardless of location, and seamlessly convert visual explorations into structured documentation addresses the key limitations of traditional starbursting while preserving its rigorous methodology.
The most successful product teams recognize that thorough exploration through systematic questioning ultimately accelerates development by preventing rework, aligning stakeholders, and ensuring all critical factors are considered before resources are committed. By integrating starbursting into your product development workflow, you can make more informed decisions, build better products, and avoid the common pitfall of solving the wrong problems perfectly.
Learn More
- Starbursting Technique: A Comprehensive Guide
- How to Run Better Brainstorming Meetings
- Product Development Methodologies Compared
- AI-Powered Mind Mapping with ClipMind
- Visual Thinking Tools for Product Managers
FAQs
-
How is starbursting different from other brainstorming techniques? Starbursting focuses exclusively on generating questions rather than solutions, using a structured framework of Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How categories. This ensures comprehensive exploration before solution development begins, unlike traditional brainstorming that often jumps straight to answers.
-
Can starbursting work for individual brainstorming or does it require a team? While starbursting benefits from multiple perspectives in team settings, individuals can use the technique effectively to challenge their own assumptions and ensure they've considered all aspects of an idea. AI tools like ClipMind can provide the "second perspective" that individuals might miss.
-
How long should a typical starbursting session last? Most productive starbursting sessions last 45-60 minutes, with time allocated for topic setup (5 minutes), question generation (30-40 minutes), and organization/next steps (10-15 minutes). Complex topics may benefit from multiple shorter sessions focused on different aspects.
-
What types of product decisions benefit most from starbursting? Starbursting is particularly valuable for foundational product decisions like feature prioritization, market entry strategies, user experience design approaches, and technical architecture choices. It's less useful for tactical decisions with limited variables or already well-understood constraints.
-
How do we handle questions that no one can answer during the session? Unanswerable questions represent valuable knowledge gaps that should be documented as research items. Assign these questions to specific team members with deadlines for investigation, and incorporate the findings into your product decisions once answers are available.
-
Can starbursting be combined with other product development frameworks? Yes, starbursting complements many product frameworks beautifully. Use it before SWOT analysis to ensure comprehensive factor identification, before Lean Canvas to explore all business model elements, or prior to user story mapping to identify all relevant user perspectives and scenarios.
-
How does AI enhancement improve traditional starbursting? AI tools like ClipMind accelerate starbursting by automatically generating relevant questions, suggesting follow-up inquiries based on team inputs, identifying potential gaps in question coverage, and helping organize questions into actionable frameworks. This reduces setup time while improving question quality and comprehensiveness.
