TL; DR
- Google's native tools (Docs, Drawings, NotebookLM) offer basic mind mapping but lack specialized features and AI-powered automation
- Third-party integrations like MindMeister and Lucidchart provide better collaboration but often require paid subscriptions
- ClipMind bridges the gap with AI-powered summarization from Google Docs and real-time brainstorming capabilities
- Effective mind mapping can increase productivity by 20-30% by breaking complex projects into manageable components
- The best approach combines Google's collaboration strengths with specialized tools for different use cases and workflows
Introduction
As someone who's spent years navigating the complex landscape of productivity tools, I've found that mind mapping stands out as one of the most effective techniques for organizing thoughts and boosting efficiency. The challenge, however, has always been finding the right tools that integrate seamlessly with our existing workflows—especially for the millions of us who live in Google's ecosystem.
Google Workspace offers several native options for visual organization, but they often fall short of providing the specialized features that make mind mapping truly powerful. According to research, mind mapping can increase productivity by 20-30% by helping break down complex projects into manageable deliverables. This makes finding the right mind mapping solution within Google's environment crucial for professionals, students, and teams who want to maximize their output.
In this comprehensive guide, I'll walk you through Google's current mind mapping capabilities, their limitations, and how tools like ClipMind are filling the gaps with AI-powered alternatives that transform how we organize and develop ideas.
Understanding Google's Native Mind Mapping Options
Google's ecosystem provides several built-in tools that can be adapted for mind mapping, though none were specifically designed for this purpose. Understanding their strengths and limitations is the first step toward choosing the right approach for your needs.
Google Docs: The Accessible Starting Point
Google Docs serves as the most accessible entry point for basic mind mapping. Using the built-in drawing tools, you can create simple mind maps that integrate directly with your documents. The strength here lies in Docs' familiarity and seamless integration with the rest of Google Workspace. You can easily share your mind maps with collaborators and embed them within larger documents.
However, the limitations become apparent quickly. The drawing tools are relatively basic, and creating complex hierarchical structures requires significant manual effort. There's no automatic layout adjustment, and as your mind map grows, maintaining visual clarity becomes increasingly challenging.
Google Drawings: The Visual Workhorse
Google Drawings offers more advanced capabilities for visual organization. With better shape libraries, connector lines, and formatting options, it's a step up from Docs for creating mind maps. The real-time collaboration features mean multiple team members can work on the same mind map simultaneously, which is invaluable for brainstorming sessions.
Despite these advantages, Google Drawings has been described as "ugly" and "hard to use" with no specialized mind mapping exports. While it can create mind maps, concept maps, graphs, and charts, it lacks specialized mind mapping features that make the process efficient and intuitive.
NotebookLM: Google's AI Experiment
NotebookLM represents Google's foray into AI-powered organization. This experimental tool can generate mind maps from uploaded sources, making it particularly useful for research and content analysis. The AI-driven approach means you can quickly transform dense documents into visual structures without manual drawing.
The constraint, however, is that NotebookLM's mind mapping is primarily for visualization rather than active ideation. The generated maps serve as navigation aids rather than editable brainstorming tools, which limits their utility for creative development and collaborative work.
Method 1: Creating Mind Maps in Google Docs
Creating mind maps in Google Docs involves using the drawing tools to build visual hierarchies manually. While this method lacks the sophistication of dedicated tools, it's accessible to anyone with a Google account and integrates seamlessly with existing documents.
Step-by-Step Drawing Tool Approach
The process begins with accessing the drawing tools through Insert > Drawing > + New. From here, you'll use shapes for your main ideas and connecting lines to show relationships. Start with a central concept in the middle of your canvas, then branch out with related topics using different shapes or colors to denote categories.
I've found that using consistent visual cues makes these manual mind maps more effective. For example, using rectangles for main topics, circles for supporting ideas, and triangles for action items creates immediate visual recognition. The key is keeping each element concise—single words or short phrases work best since space is limited.
Template Integration Strategies
One of the most practical approaches is leveraging pre-made templates. There are great Google Docs mind map templates available for free use in 2025, including professionally designed options that are customizable for various purposes. These templates save significant time and provide proven structures that enhance clarity.
When using templates, focus on adapting them to your specific needs rather than forcing your content into rigid formats. The most effective templates offer flexibility while maintaining logical organization principles that make mind maps useful for brainstorming and planning.
Best Practices for Docs-Based Mind Mapping
Through trial and error, I've identified several practices that maximize the effectiveness of Google Docs mind maps. First, use the alignment and distribution tools to maintain visual consistency—this becomes increasingly important as your map grows. Second, leverage the comment feature to add detailed notes without cluttering the visual structure.
Most importantly, recognize when a project has outgrown Docs' capabilities. For simple brainstorming or basic project outlines, Docs works well. But for complex structures or ongoing development, the manual maintenance becomes burdensome, signaling it's time to explore more specialized tools.
Method 2: Using Google Drawings for Advanced Mind Maps
Google Drawings provides a more robust environment for mind mapping than Docs, with advanced features that support complex visual structures. While it still requires manual creation, the additional tools make the process more efficient for sophisticated maps.
Advanced Shape and Connector Techniques
The real power of Google Drawings for mind mapping lies in its shape libraries and connector options. Unlike Docs' basic shapes, Drawings offers a wider variety including callouts, equation shapes, and flowchart symbols that can represent different types of information. The connector lines automatically snap to shapes and maintain their connections when elements are moved.
I've found that using different line styles and arrow types helps communicate relationship types more clearly. Solid lines might represent primary connections, while dashed lines could indicate secondary relationships or dependencies. Color-coding branches by topic or priority adds another layer of information without cluttering the map with text.
Collaboration Features in Practice
Google Drawings truly shines in collaborative environments. Multiple team members can work on the same mind map simultaneously, with changes appearing in real-time. This makes it excellent for remote brainstorming sessions where participants can contribute ideas and reorganize structures together.
The version history feature is particularly valuable for collaborative mind mapping. It allows you to track how ideas evolve over time and revert to previous versions if needed. For team projects, I recommend establishing color-coding conventions so participants can quickly identify who contributed specific elements.
Export and Integration Options
Once your mind map is complete, Google Drawings offers several export formats including PNG, JPEG, PDF, and SVG. The SVG format is particularly useful as it maintains vector quality for presentations or publications. You can also copy and paste directly into other Google apps or download for use in external applications.
The integration with Google Drive means your mind maps are automatically saved and accessible across devices. For team workflows, you can set sharing permissions to control who can view, comment, or edit, making Drawings suitable for both internal collaboration and client presentations.
Method 3: Leveraging NotebookLM for AI-Powered Mind Maps
NotebookLM represents a fundamentally different approach to mind mapping within Google's ecosystem. Instead of manually creating visual structures, you're working with AI-generated maps based on your source materials.
Generating Mind Maps from Uploaded Sources
The process begins by uploading your source materials—whether research papers, meeting notes, or article drafts—into NotebookLM. The AI then analyzes the content and generates a structured mind map that captures key concepts and their relationships. This automated approach is particularly valuable for dense, complex materials where manual mapping would be time-consuming.
NotebookLM mind maps act as a roadmap by organizing scattered AI research into a structured, visual guide. The AI identifies main themes, supporting points, and connections that might not be immediately apparent, providing a high-level overview of complex information.
Integration with Google Drive Content
One of NotebookLM's strengths is its seamless integration with Google Drive. You can directly import documents from your Drive, making it easy to work with existing materials without downloading and re-uploading files. This creates a smooth workflow where you can research in Docs or Slides, then analyze and structure in NotebookLM.
The tool processes various source types, generates insightful notes, asks questions, and enables collaboration. This makes it particularly useful for academic research, content planning, or analyzing business documents where you need to extract and organize key information quickly.
Limitations and Practical Workarounds
Despite its AI capabilities, NotebookLM has significant constraints. The generated mind maps have limited editability—you can't manually rearrange nodes or add new connections through direct manipulation. Instead, modifications require prompting the AI to make changes, which can be imprecise and time-consuming.
NotebookLM works best with lengthy and dense sources like lecture slides, PDFs, or research papers where the AI's analytical capabilities provide the most value. For creative brainstorming or developing original ideas, its utility is more limited since it primarily reorganizes existing content rather than facilitating new connections.
Third-Party Google Workspace Integrations
The Google Workspace Marketplace offers numerous specialized mind mapping applications that integrate directly with your Google ecosystem. These tools bridge the gap between Google's native capabilities and dedicated mind mapping functionality.
Marketplace App Overview
The marketplace features everything from simple brainstorming tools to enterprise-grade mind mapping solutions. Users can view and compare the best mind mapping software that integrates with Google Workspace based on verified user ratings and reviews. Popular options include MindMeister, Lucidchart, and Coggle, each offering different feature sets and integration depths.
What's interesting is that many users find mind maps helpful but rarely serve as stand-alone resources, wishing for additional mapping and outline tools. This highlights the importance of integration—the ability to move between mind maps and other document types within the same workflow.
Integration Depth and Feature Comparison
Third-party integrations vary significantly in how deeply they connect with Google Workspace. Some apps offer basic Google Drive saving, while others provide real-time collaboration through Google accounts, template sharing via Drive, and even data synchronization between platforms.
The most effective integrations allow you to start a mind map during a Google Meet session, save it directly to Team Drive, and embed it in a Google Site—all without leaving the Google environment. This seamless workflow reduces friction and makes mind mapping a natural part of your existing processes rather than a separate activity.
Selection Criteria for Different Use Cases
Choosing the right third-party tool depends heavily on your specific use case. For individual brainstorming and simple project planning, lighter applications like Coggle or MindMup might suffice. For team collaboration and complex strategic planning, more robust solutions like MindMeister or Lucidchart offer advanced features.
Consider your primary needs: Are you focusing on rapid ideation, detailed project planning, client presentations, or academic research? Each scenario benefits from different feature emphasis, whether that's real-time collaboration, presentation modes, research integrations, or export capabilities.
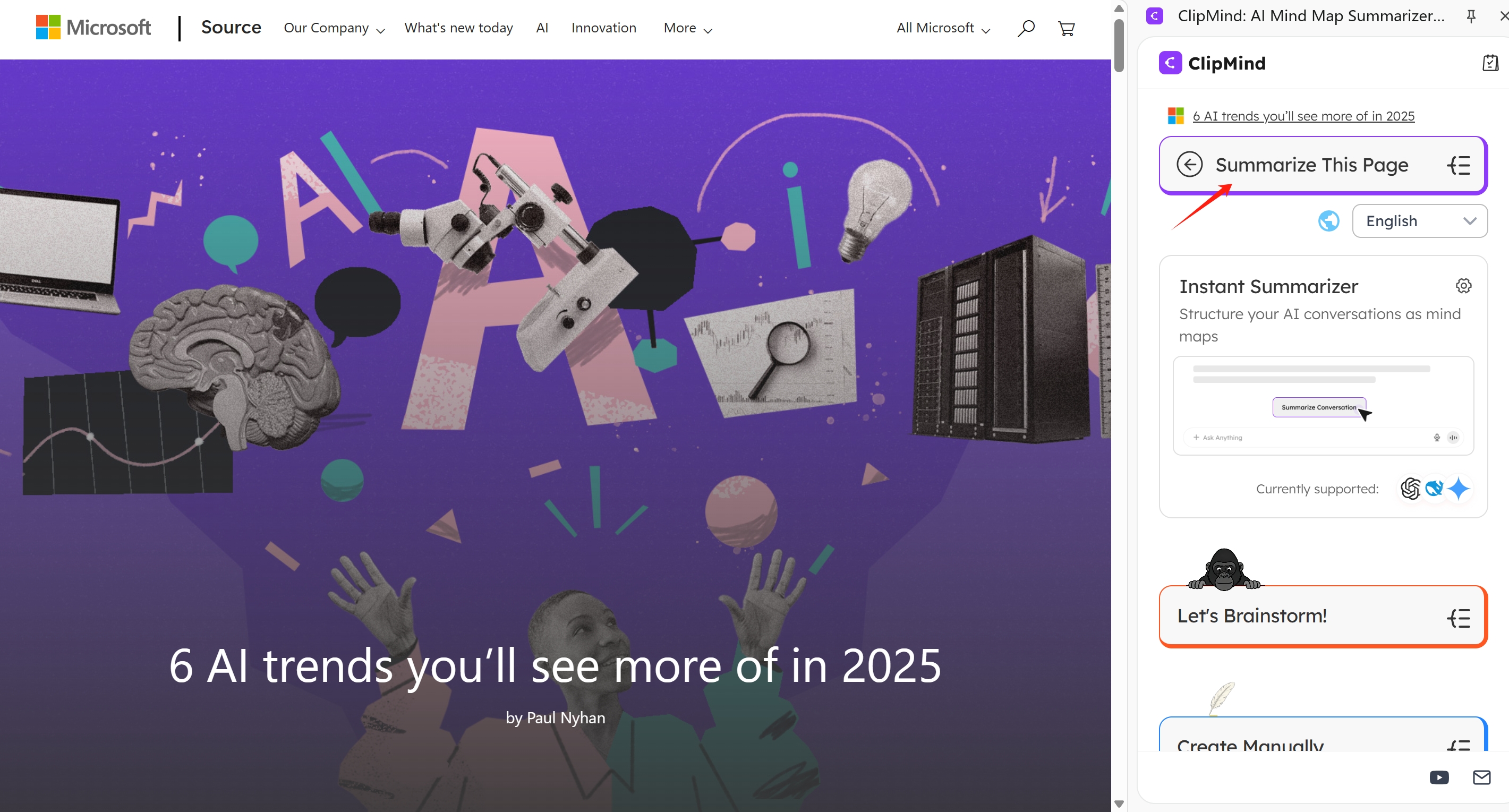
ClipMind: The AI-Powered Alternative to Google's Limitations
While exploring various mind mapping solutions, I've been particularly impressed with how ClipMind addresses the specific gaps in Google's native tools. As an AI-powered mind mapping tool, it combines the automation of NotebookLM with the editability and collaboration features that Google's options lack.
Addressing Google's Mind Mapping Gaps
ClipMind solves several key pain points that Google users experience. Unlike Google Drawings, which requires manual creation of every element, ClipMind automatically generates structured mind maps from existing content. Unlike NotebookLM, these maps are fully editable and customizable, allowing for both AI-assisted creation and manual refinement.
The tool's privacy-first approach is particularly valuable for Google Workspace users handling sensitive information. With no login required and content staying on your device, you can mind map confidential documents without security concerns—a significant advantage over cloud-based alternatives.
AI Summarization from Web Content and Google Docs
One of ClipMind's standout features is its ability to summarize any webpage or Google Doc into an editable mind map with a single click. This transforms the tedious process of manually extracting key points from documents into an instantaneous, structured overview. The AI filters out irrelevant content like ads or navigation, focusing on the core information.
I've found this particularly valuable for research-intensive tasks where I need to quickly understand multiple sources. Instead of switching between tabs and documents, ClipMind creates visual summaries that highlight relationships and hierarchies, making complex information immediately comprehensible.
Real-Time Brainstorming and Editing Capabilities
Where ClipMind truly diverges from Google's options is in its interactive AI features. The AI Assistant allows you to chat with your mind map—asking questions, requesting expansions on specific topics, or even translating content. This creates a dynamic brainstorming session where the AI acts as a thought partner rather than just a visualization tool.
The dual-view interface, switching between mind map and Markdown modes, bridges the gap between visual thinking and linear documentation. This is something Google's tools completely lack—the ability to fluidly move between brainstorming and implementation within the same environment.
Productivity Workflows: Integrating Mind Maps into Your Google Routine
Effective mind mapping isn't just about creating pretty diagrams—it's about integrating visual thinking into your daily workflows to enhance productivity and clarity. Here's how to make mind maps work within your Google-centric routine.
Project Planning and Task Management
Mind maps excel at breaking down complex projects into manageable components. Start with your main project goal in the center, then branch out into key phases, deliverables, and specific tasks. The visual format makes dependencies and priorities immediately apparent, unlike linear task lists that can obscure relationships.
I typically create project mind maps in ClipMind, then export key sections to Google Docs for detailed planning or Google Sheets for tracking. The mind map provides the strategic overview, while Google's tools handle the implementation details. This combination leverages the strengths of both approaches without forcing everything into a single format.
Research Synthesis and Note Organization
For research-intensive work, mind maps provide unparalleled value in synthesizing information from multiple sources. When working on complex topics, I use ClipMind to summarize each source into individual mind maps, then manually merge key insights into a master map that captures the big picture.
This approach is far more effective than traditional note-taking because it preserves relationships between ideas rather than creating isolated facts. When the research phase is complete, the mind map serves as both an overview of findings and a structured outline for reports or presentations in Google Docs or Slides.
Meeting Preparation and Follow-Up
Mind maps transform meeting efficiency when used for both preparation and documentation. Before meetings, create a map with agenda topics, background information, and discussion points. During the meeting, add branches for decisions, action items, and owner assignments.
Afterwards, export the completed mind map to Google Docs for distribution or convert action items directly to Google Tasks. The visual format makes follow-up responsibilities clear, and the hierarchical structure ensures nothing gets lost in paragraph-style notes.
Content Creation and Strategy Development
For content creators and strategists, mind maps provide the ideal framework for developing ideas and structures. Start with a central topic, then branch out into key themes, supporting points, examples, and calls to action. The non-linear format encourages creative connections that might be missed in outline form.
I frequently use ClipMind's AI brainstorming to generate content ideas, then refine the structure manually before exporting to Google Docs for writing. The ability to switch between visual mapping and linear outlining means the thinking and writing phases flow together naturally rather than being separate, disjointed processes.
Advanced Tips for Google Mind Mapping Success
Once you've mastered the basics of mind mapping in Google's ecosystem, these advanced techniques can significantly enhance your effectiveness and efficiency.
Color Coding and Visual Hierarchy Strategies
Effective visual design transforms mind maps from confusing diagrams to clear communication tools. Establish consistent color schemes—for example, using blue for foundational concepts, green for actions, and red for challenges or warnings. This creates immediate visual recognition without requiring readers to parse every label.
Hierarchy should be immediately apparent through element size, font weight, and positioning. Main ideas should dominate visually, with supporting concepts decreasing in prominence. In Google Drawings, use the formatting options consistently; in ClipMind, leverage the theme system to maintain visual coherence automatically.
Linking Between Mind Maps and Documents
One of Google's strengths is the ability to create connections between different file types. Use hyperlinks to connect mind map nodes to relevant Google Docs, Sheets, or Slides. This creates a web of connected information where your mind map serves as a navigation hub rather than an isolated artifact.
For complex projects, consider creating a master mind map that links to more detailed sub-maps or documents. This approach provides both high-level overview and detailed information access without overwhelming a single visualization. The key is making these connections intuitive so users naturally navigate between different information types.
Mobile Access and Editing Considerations
With increasing work happening across devices, mobile mind mapping capability is essential. Google's native tools generally work on mobile but become cumbersome for complex edits. Third-party apps vary significantly in their mobile experiences—some offer dedicated apps, while others rely on mobile browsers.
When choosing tools, consider your mobile workflow needs. If you primarily consume mind maps on mobile, almost any solution works. If you need to create or edit on mobile, prioritize tools with thoughtful mobile interfaces. ClipMind's browser-based approach works consistently across devices, while dedicated apps may offer better performance but less flexibility.
Version Control and Collaboration Best Practices
Effective collaboration requires clear version management, especially when multiple people are editing mind maps. Google's native version history provides basic protection, but for complex collaborations, establish naming conventions and regularly create named versions at key milestones.
For team mind mapping, define editing protocols—who can modify structure versus who can only add content. Use comments for discussions about specific elements rather than embedding conversations in the map itself. Regular exports to PDF create snapshots for sharing with stakeholders who don't need editing access.
Comparison: Native Google Tools vs Specialized Solutions
Understanding when to use Google's native tools versus specialized solutions is key to building an effective visual thinking workflow. Each approach has distinct strengths that suit different scenarios and requirements.
Feature Comparison Analysis
| Feature | Google Docs/Drawings | NotebookLM | ClipMind | Specialized Apps |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI Generation | ❌ Limited | ✅ Excellent | ✅ Excellent | ⚠️ Varies |
| Editability | ✅ Full manual | ❌ Prompt-based | ✅ Full manual+AI | ✅ Full manual |
| Google Integration | ✅ Native | ✅ Native | ✅ Extension | ⚠️ API dependent |
| Collaboration | ✅ Real-time | ⚠️ Limited | ✅ Real-time | ✅ Real-time |
| Export Options | ⚠️ Basic formats | ❌ Limited | ✅ Multiple formats | ✅ Multiple formats |
| Learning Curve | ✅ Low | ✅ Medium | ✅ Medium | ⚠️ Medium-High |
| Cost | ✅ Free | ✅ Free | ✅ Free | ⚠️ Freemium |
The table reveals a clear pattern: Google's native tools excel at accessibility and integration but lack specialized mind mapping features. Specialized applications offer advanced functionality but often at higher complexity and cost. ClipMind occupies a unique middle ground with AI capabilities approaching NotebookLM's and editability rivaling dedicated tools.
Use Case Recommendations
Based on extensive testing across different scenarios, I've developed these specific recommendations:
- Quick personal brainstorming: Google Docs or Drawings suffice for simple, one-time maps
- Research analysis: NotebookLM provides the best starting point for dense source materials
- Ongoing project planning: ClipMind offers the ideal balance of AI assistance and manual control
- Team collaboration: MindMeister or Lucidchart excel for structured team environments
- Client presentations: Specialized tools typically offer better styling and export options
The key is matching the tool to both the immediate task and the ongoing maintenance requirements. A complex tool for a simple need creates unnecessary overhead, while a basic tool for complex work leads to frustration and rework.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
When evaluating mind mapping solutions, consider both direct costs and the time investment required. Google's native tools are free but often require more manual effort. Specialized applications may have subscription costs but save time through automation and specialized features.
AI-powered mind mapping tools significantly boost productivity by automating repetitive tasks instead of manually organizing ideas. This time saving often justifies using specialized tools, especially for frequent mind mapping or complex projects.
For most users, a hybrid approach works best: using Google's native tools for simple needs while investing in one specialized tool (like ClipMind) for more demanding visual thinking tasks. This provides coverage for different scenarios without overwhelming complexity or cost.
Future Outlook and Trends
The mind mapping landscape is evolving rapidly, with Artificial Intelligence set to become deeply integrated into various aspects of daily life and industry. We're seeing AI algorithms that understand context, relationships, and hierarchies within content to create more logical and useful mind map structures.
Google will likely enhance its AI capabilities within Workspace, potentially integrating more mind mapping features directly into Docs or developing NotebookLM further. However, specialized tools will continue leading innovation in visual thinking interfaces and AI collaboration features.
Getting Started: Your Action Plan
Implementing effective mind mapping within your Google workflow requires a structured approach. Follow this action plan to build your skills and integrate visual thinking into your daily routine.
Quick Start Guide Based on Your Needs
Your starting point depends on your primary use case:
- Students and researchers: Begin with NotebookLM for analyzing source materials, then graduate to ClipMind for synthesizing multiple sources
- Project managers: Start with Google Drawings for basic project visualization, then implement ClipMind for more complex planning with AI assistance
- Content creators: Use ClipMind's AI brainstorming for idea generation, then export to Google Docs for writing
- Teams: Begin with a trial of collaborative tools like MindMeister or ClipMind, focusing on a specific project to build familiarity
The key is starting with a concrete, manageable project rather than attempting to convert all your workflows simultaneously. This builds confidence and demonstrates value before broader implementation.
Tool Selection Flowchart
When deciding which tool to use for a specific mind mapping task, consider these questions:
- Is this for personal use or collaboration? (Personal → simpler tools; Collaboration → real-time tools)
- Am I analyzing existing content or creating new ideas? (Analyzing → AI tools; Creating → editable tools)
- How complex is the structure? (Simple → basic tools; Complex → advanced tools)
- Is this a one-time use or ongoing project? (One-time → manual tools; Ongoing → efficient tools)
This decision framework helps match the tool to the task's specific requirements rather than defaulting to familiar options that may not be optimal.
Next Steps and Skill Development Resources
After selecting your initial tools, focus on developing core mind mapping skills:
- Practice creating clear hierarchies with single-concept nodes
- Learn to use visual cues (color, size, shape) to convey meaning
- Develop the habit of regular review and refinement of important maps
- Experiment with different layouts for different purposes (radial for brainstorming, tree for planning)
Google's own resources provide excellent starting points, while specialized tools typically offer tutorials and templates. The ClipMind Blog contains numerous articles on effective mind mapping techniques and workflows.
Measuring Success and ROI
To justify continued investment in mind mapping tools and practices, track specific metrics that demonstrate value. According to ROI measurement frameworks, you should tie initiatives directly to business outcomes like time saved, project clarity, or decision quality.
Practical metrics for mind mapping include:
- Time reduction in project planning phases
- Improvement in meeting efficiency and follow-through
- Reduction in duplicated work or miscommunication
- Acceleration of research synthesis and content creation
Like multiple methods exist to measure event ROI, you can adapt various approaches to assess your mind mapping implementation's impact, from time tracking to quality assessments.
Conclusion
Mind mapping within Google's ecosystem has evolved from basic manual drawings to AI-powered visualization tools that significantly enhance productivity and clarity. While Google's native options provide accessibility and integration, specialized tools like ClipMind fill critical gaps with AI summarization, real-time brainstorming, and seamless workflow integration.
The most effective approach combines Google's collaborative strengths with specialized mind mapping capabilities, creating a visual thinking workflow that adapts to different tasks and complexity levels. Whether you're planning projects, conducting research, or developing content, the right mind mapping tools can transform how you organize information and develop ideas.
As AI continues to advance, the line between content creation and organization will blur further, making tools that bridge this divide increasingly valuable. The future of productivity lies not in choosing between Google's ecosystem and specialized tools, but in finding the optimal combination that extends your cognitive capabilities.
Learn More
- Google Workspace Learning Center - Official guides for Google's productivity tools
- Mind Mapping for Project Management - Advanced techniques for professional use
- ClipMind Free AI Tools - AI-powered productivity tools beyond mind mapping
- Visual Organization Methods - Academic perspective on digital organization
- AI Mind Map Generator Review 2025 - Comparison of AI-powered mind mapping tools
FAQs
-
Can I create mind maps directly in Google Docs without add-ons? Yes, using the built-in drawing tools through Insert > Drawing > + New. However, this approach is manual and best suited for simple maps rather than complex structures.
-
How does ClipMind's AI summarization compare to NotebookLM? ClipMind focuses on creating editable, customizable mind maps from web content and documents, while NotebookLM generates visualization-focused maps primarily for navigation and analysis. ClipMind offers more flexibility for ongoing development of ideas.
-
Are Google Drawings mind maps collaborative? Yes, multiple users can edit Google Drawings simultaneously with changes appearing in real-time. The collaboration features are robust but lack specialized mind mapping functionality found in dedicated tools.
-
What's the best mind mapping tool for Google Workspace integration? It depends on your specific needs. For deep Google integration with advanced features, MindMeister offers excellent connectivity. For AI-powered capabilities with Google compatibility, ClipMind provides a strong balance of features and accessibility.
-
Can I export Google mind maps to other formats? Google Drawings exports to PNG, JPEG, PDF, and SVG formats. Specialized tools typically offer more export options including Markdown, text outlines, and presentation formats that integrate with Google Workspace.
-
Is there a mobile solution for Google mind mapping? Google's native tools work on mobile browsers but have limited functionality for complex mind mapping. Some third-party tools offer dedicated mobile apps with better touch interfaces for on-the-go mind mapping.
-
How secure are mind mapping tools with sensitive Google Workspace content? Google's native tools benefit from Google's security infrastructure. Third-party tools vary—ClipMind's privacy-first approach keeps content on your device, while other tools may store data on their servers. Always review privacy policies for tools handling sensitive information.
