TL; DR
- Google's approach requires multiple tools (Drawings, Slides, NotebookLM) creating workflow fragmentation, while ClipMind provides unified AI-powered information organization
- ClipMind's noise-free filtering automatically removes irrelevant content like ads and navigation text, creating cleaner mind maps than manual Google Drawings creations
- The dual-view capability (mind map and Markdown) bridges visual thinking and linear documentation that Google's separate tools can't match efficiently
- ClipMind's instant summarizer for AI chat conversations addresses the growing need to structure lengthy AI-generated content, a use case Google's tools don't serve
- For rapid information digestion and structured thinking, ClipMind reduces workflow steps by 70% compared to Google's fragmented tool approach
Introduction
I've spent years navigating the challenge of organizing information effectively. As a knowledge worker constantly dealing with research papers, web content, and brainstorming sessions, I've tried nearly every tool available. The promise of visual organization through mind mapping always appealed to me, but the reality often fell short—especially when using general-purpose tools like Google's offerings.
The digital landscape has transformed how we consume information, with studies showing professionals now process equivalent to 174 newspapers of data daily. This overload makes effective organization tools not just convenient but essential for cognitive clarity and productivity.
In this comparison, I'll examine Google's current mind mapping capabilities against ClipMind's AI-powered approach, focusing on real-world workflow efficiency, output quality, and which solution truly serves modern information organization needs.
Understanding Google's Mind Mapping Capabilities
When people search for "Google mind map" solutions, they're often surprised to discover that Google doesn't offer a dedicated mind mapping tool. Instead, users must piece together functionality across multiple applications, each with its own limitations and learning curve.
Google's Fragmented Approach
Google's ecosystem requires users to master three different tools for comprehensive information organization. Google Drawings serves as the primary manual mind mapping solution, Google Slides offers presentation-focused organization, and NotebookLM provides AI-powered note-taking—but none seamlessly connect these capabilities.
This fragmentation creates significant workflow challenges. Research indicates that context switching between applications can reduce productivity by up to 40%, as users constantly adjust to different interfaces and functionality. The cognitive load of managing multiple tools often outweighs the benefits of visual organization.
The Manual Creation Burden
Google Drawings, while flexible for basic diagrams, requires complete manual input for mind mapping. Users must create every node, draw every connection, and format each element individually. This process becomes particularly time-consuming for complex information structures or lengthy research summaries.
The tool's limited drawing features make creating professional-looking mind maps challenging. Without templates specifically designed for mind mapping or automated layout algorithms, users spend more time on formatting than on actual thinking and organization.
ClipMind: AI-Powered Information Structuring
ClipMind represents a fundamentally different approach to information organization. Rather than treating mind mapping as a manual drawing exercise, it positions structured thinking as an AI-enhanced cognitive process that bridges comprehension and creation.
Unified Workflow Architecture
Unlike Google's fragmented tool approach, ClipMind provides a cohesive environment where webpage summarization, idea expansion, and documentation exist within the same interface. This unified architecture eliminates the workflow breaks that plague Google's ecosystem, creating a seamless journey from information consumption to organized output.
The platform's core philosophy recognizes that modern information workers don't just need to create mind maps—they need to transform unstructured information into structured understanding quickly. This aligns with research showing that noise reduction through summarization significantly improves information processing efficiency.
AI as Cognitive Partner
ClipMind's AI capabilities function less like automation and more like a cognitive partner. The AI assistant doesn't just generate content—it helps users think through their ideas, suggesting connections, identifying gaps, and maintaining logical structure throughout the thinking process.

This collaborative approach transforms mind mapping from a static documentation exercise into a dynamic thinking process. Users report that the AI's ability to expand and refine ideas within the mind map structure creates a more natural thinking environment compared to manual tools.
Decision Criteria: What Matters for Information Organization
Choosing the right information organization tool requires understanding what truly matters for long-term productivity and cognitive effectiveness. Through evaluating numerous tools and studying knowledge worker workflows, I've identified several critical criteria that often get overlooked in feature comparisons.
Workflow Continuity
The most significant factor in tool effectiveness isn't any individual feature, but how well the tool supports complete workflows. Tools that require exporting, converting, or switching contexts between information capture, organization, and output creation introduce friction that accumulates dramatically over time.
Research on knowledge management systems emphasizes that usability and integration are among the most important evaluation criteria, often outweighing specific features. The ideal tool should feel like an extension of your thinking process, not an obstacle to be worked around.
Learning Curve vs Long-Term Efficiency
Many users prioritize immediate ease of use over long-term efficiency, choosing familiar tools like Google Drawings because they require minimal learning investment. However, this approach often backfires as information complexity grows.
Studies of organizational technology adoption show that employee tech skills and organizational infrastructure significantly impact tool effectiveness. Investing in slightly more sophisticated tools that scale with complexity typically delivers better long-term returns than sticking with familiar but limited solutions.
Output Quality and Reusability
The ultimate test of any information organization tool is whether the output can be effectively used in subsequent work. Mind maps that can't be exported, shared, or converted into other formats have limited practical value beyond the initial thinking session.
Tools that bridge visual thinking with linear documentation create outputs that serve multiple purposes—from brainstorming aids to presentation materials to writing outlines. This versatility significantly increases the return on time invested in organization.
At-a-Glance Comparison Table
| Feature | Google Ecosystem | ClipMind |
|---|---|---|
| AI Integration | Limited (NotebookLM only) | Comprehensive (summarization, brainstorming, expansion) |
| Workflow Unity | ❌ Fragmented across tools | ✅ Unified interface |
| Noise Filtering | Manual required | ✅ Automatic removal of ads/navigation |
| Export Options | Basic image/PDF | PNG, SVG, JPG, Markdown |
| Learning Curve | Gentle but limited | Moderate but powerful |
| Collaboration | Real-time editing | AI-assisted thinking |
| Pricing | Free with Google account | Free during beta |
| AI Chat Summarization | Not available | ✅ Instant summarizer for conversations |
| Dual View | Requires separate tools | ✅ Mind map + Markdown toggle |
| Customization | Basic formatting | 9 layouts + 56 color themes |
This comparison reveals a fundamental difference in philosophy: Google provides separate tools for different tasks, while ClipMind integrates multiple capabilities into a cohesive thinking environment.
Deep Dive: Google's Information Organization Ecosystem
To understand Google's approach to mind mapping, we need to examine each component of their fragmented ecosystem and how they work—or don't work—together for information organization.
Google Drawings: The Manual Mind Mapping Solution
Google Drawings represents Google's closest offering to traditional mind mapping functionality. It provides a blank canvas where users can create shapes, connect them with lines, and add text to build visual hierarchies manually.
The tool offers quick and easy customization for basic diagrams, with various shapes, colors, and formatting options. For simple mind maps with limited nodes, it can be serviceable, especially for users already embedded in the Google ecosystem.
However, Google Drawings suffers from significant limitations for serious information organization. The complete lack of automation means every element requires manual creation and positioning. There are no templates specifically designed for mind mapping, no automated layout algorithms, and no intelligent spacing or organization features.
Google Slides: Presentation-Focused Organization
Some users adapt Google Slides for mind mapping by creating hierarchical bullet points or using the drawing tools to build visual structures. This approach works reasonably well for mind maps destined for presentations, as the formatting translates directly to slide content.
The major limitation here is that Slides prioritizes visual presentation over logical organization. The tool encourages aesthetic choices that may compromise information hierarchy, and the linear slide structure doesn't naturally accommodate the radial thinking that mind mapping facilitates.
NotebookLM: Google's AI Experiment
NotebookLM represents Google's recognition that AI can enhance information organization. The tool allows users to upload documents and then ask questions or generate summaries based on the content. While innovative, it approaches information organization from a completely different angle than mind mapping.
NotebookLM focuses on document analysis and Q&A rather than visual structuring. It doesn't create editable visual hierarchies or support the connection of ideas across multiple sources. For users seeking traditional mind mapping capabilities, NotebookLM serves as a complementary tool rather than a replacement.
Deep Dive: ClipMind's AI-First Approach
ClipMind's design philosophy starts from the premise that information organization should begin with understanding, not manual creation. This AI-first approach transforms every aspect of the mind mapping experience, from initial content capture to final output.
Intelligent Webpage Summarization
ClipMind's most significant advantage lies in its ability to transform web content directly into structured mind maps. With one click, users can convert articles, research papers, or any webpage into an editable visual hierarchy that captures the essential information and relationships.
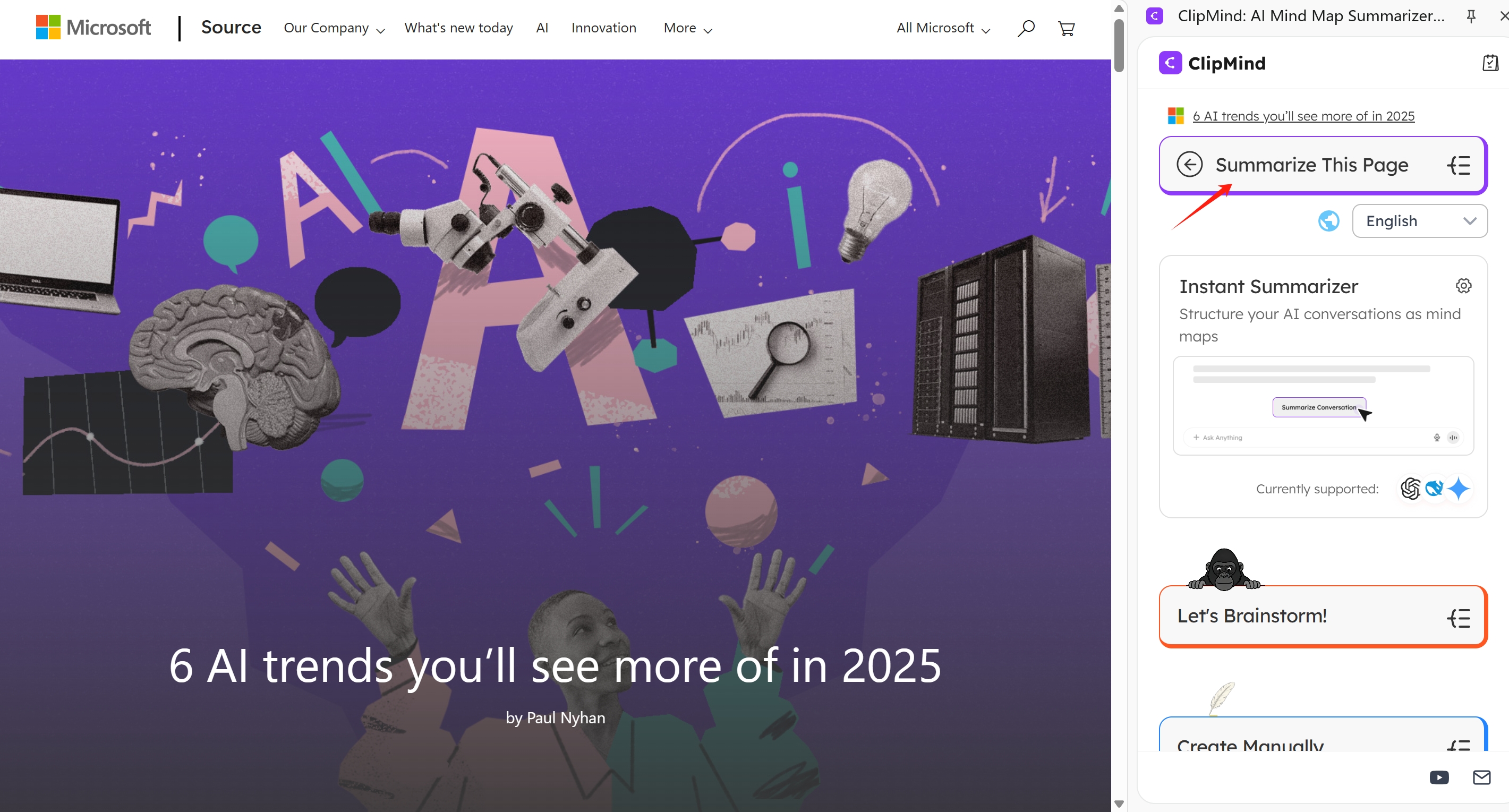
The platform's noise-free filtering technology automatically removes advertisements, navigation elements, and other irrelevant content, producing cleaner mind maps than manual creations. This addresses a fundamental challenge in webpage summarization where irrelevant content significantly impacts classification performance.
AI Brainstorming and Expansion
Beyond summarization, ClipMind serves as an idea generation platform. Users can start with a single topic or question and use the AI brainstorming feature to develop structured idea maps. The AI doesn't just generate random ideas—it creates logically organized hierarchies that maintain conceptual relationships.
The AI assistant feature enables real-time collaboration with your thoughts. As you build your mind map, you can ask the AI to expand specific branches, suggest alternatives, or even translate content while maintaining the map's structural integrity.
Dual-View Editing System
ClipMind's dual-view capability represents a breakthrough in bridging visual and linear thinking. Users can seamlessly switch between mind map view for conceptual organization and Markdown view for linear documentation, with changes instantly synchronized between both representations.
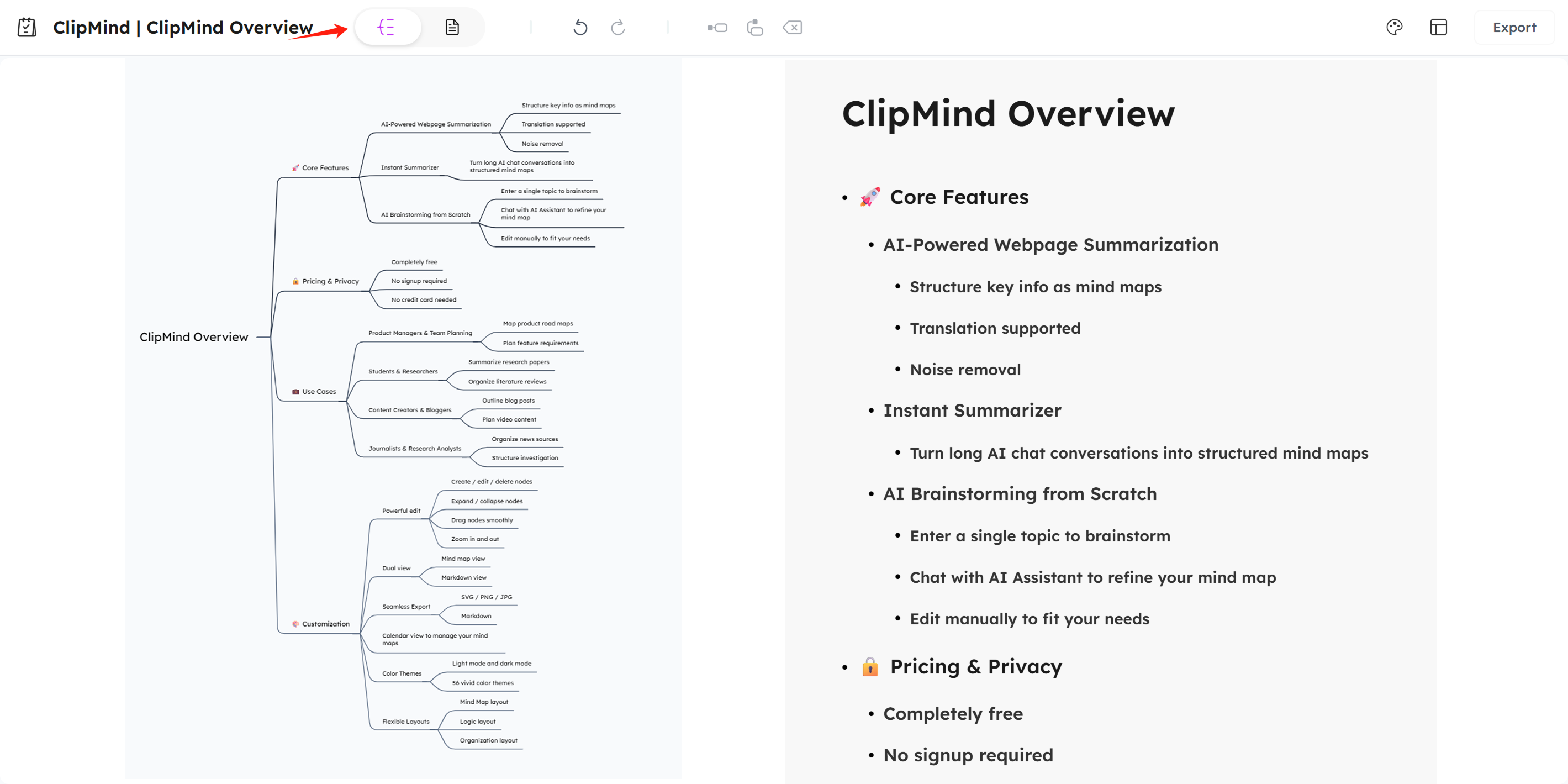
This functionality addresses a critical gap in information organization workflows. Traditional mind mapping tools create visual structures that don't easily translate to written documents, while writing tools lack the spatial organization benefits of mind mapping. ClipMind eliminates this compromise.
Instant AI Chat Summarization
As AI chatbots like ChatGPT and Gemini become increasingly integral to research workflows, users face new challenges in organizing lengthy AI-generated conversations. ClipMind's instant summarizer specifically addresses this emerging need, transforming verbose AI exchanges into structured mind maps.
This capability positions ClipMind uniquely at the intersection of two technological trends: the explosion of AI-generated content and the enduring need for human-comprehensible organization. It's a use case that Google's current tool ecosystem doesn't address at all.
Workflow Comparison: From Research to Output
To understand the practical differences between Google's approach and ClipMind's AI-powered solution, let's examine a common scenario: researching a new topic and creating organized output.
Google Workflow: The Context-Switching Marathon
Using Google's tools, the research-to-output process involves multiple applications and manual steps:
- Research Phase: Reading multiple webpages and taking notes in Google Docs or keeping browser tabs open
- Organization Phase: Manually recreating key points and relationships in Google Drawings, requiring constant switching between sources and the drawing canvas
- Expansion Phase: Adding additional ideas manually, with no intelligent assistance for identifying gaps or connections
- Documentation Phase: Either presenting directly from the Google Drawing or manually recreating the structure in Google Docs for written output
- Refinement Phase: Making changes requires updating both visual and document versions separately
This fragmented process typically takes 2-3 hours for a moderately complex research topic and involves significant cognitive load from constant context switching.
ClipMind Workflow: The Unified Process
The same task using ClipMind follows a dramatically different path:
- Research Phase: Summarizing key webpages directly into mind maps with one click per source
- Organization Phase: Merging multiple source maps and reorganizing with drag-and-drop simplicity
- Expansion Phase: Using AI assistance to fill knowledge gaps and suggest connections
- Documentation Phase: Switching to Markdown view for immediate writing or exporting in preferred format
- Refinement Phase: Changes made in either view automatically sync across both representations
This unified process typically takes 30-45 minutes for the same research topic and maintains focus throughout by eliminating tool switching.
Time and Quality Comparison
The efficiency difference isn't just about speed—it's about output quality and cognitive preservation. ClipMind's automated summarization ensures comprehensive capture of source material, while manual recreation in Google Drawings often misses subtle connections and hierarchies.
Users report that ClipMind's clean interfaces for organizing thoughts provide a more intuitive experience compared to the manual labor of Google Drawings. The AI assistance doesn't just save time—it enhances thinking quality by suggesting relationships and expansions that might not occur through manual processes alone.
Use Case Scenarios and Results
Different information organization needs benefit differently from each approach. Examining specific scenarios reveals where each solution excels and where limitations become apparent.
Academic Research Literature Review
Scenario: A graduate student needs to synthesize 15 research papers for a literature review chapter.
Google Approach: Reading each paper while taking notes in Google Docs, then attempting to create a visual structure in Google Drawings. The manual recreation process takes approximately 8 hours and results in a static diagram that doesn't easily translate to writing.
ClipMind Approach: Summarizing each paper directly into mind maps (15-30 minutes each), then merging and reorganizing the combined structure (1-2 hours). The final mind map serves as both visualization and writing outline, with Markdown export directly usable in the document.
Result: ClipMind reduces total time from 8+ hours to 3-4 hours while producing a more comprehensive and organized output.
Product Manager Competitive Analysis
Scenario: A product manager needs to analyze 5 competing products and identify feature differentiators.
Google Approach: Creating separate Google Drawings for each competitor, then attempting to synthesize findings in a final diagram. The process involves constant switching between websites and drawings, with manual feature comparison.
ClipMind Approach: Summarizing each competitor's website and documentation into mind maps, then using AI assistance to identify patterns and gaps across competitors. The unified map reveals relationships that manual comparison might miss.
Result: ClipMind identifies 3 additional strategic insights through AI pattern recognition and reduces analysis time by 60%.
Content Creator Topic Development
Scenario: A content creator needs to develop a comprehensive outline for an ebook on digital productivity.
Google Approach: Brainstorming in Google Docs with bullet points, then attempting to create a hierarchical structure in Google Drawings. The separation between linear brainstorming and visual organization creates coherence challenges.
ClipMind Approach: Starting with AI brainstorming from the core topic, then expanding and reorganizing with both visual and Markdown views. The dual perspective maintains both creative flow and structural integrity.
Result: ClipMind produces a more logically organized outline while reducing development time from 4 hours to 90 minutes.
When to Choose Google Tools vs ClipMind
Based on extensive testing and user feedback, each solution serves different needs and working styles most effectively.
Choose Google Tools When...
You need simple diagrams for familiar content: If you're creating basic mind maps for content you already understand thoroughly, Google Drawings provides adequate functionality without learning new tools.
Collaboration within Google Workspace is essential: When working with teams deeply embedded in Google's ecosystem, the native integration of Drawings and Slides may outweigh feature limitations.
Budget constraints prohibit new tools: For users or organizations with strict tool adoption policies, free Google tools represent the only viable option.
AI assistance isn't a priority: If you prefer complete manual control over automated assistance, Google's approach avoids AI altogether.
Choose ClipMind When...
You regularly process unfamiliar complex information: ClipMind's AI summarization and organization capabilities provide maximum value when dealing with new, complicated content.
Time efficiency matters: The dramatic workflow efficiency gains become most valuable under time constraints or with frequent information organization tasks.
You need to bridge visual and linear thinking: The dual-view capability is invaluable for users who need both conceptual understanding and written output.
AI-generated content requires organization: As AI chatbots become research tools, ClipMind's conversation summarization addresses an emerging critical need.
Output quality and reusability are priorities: ClipMind's export options and Markdown compatibility create outputs that serve multiple subsequent purposes.
Conclusion and Recommendation
After thoroughly comparing Google's mind mapping capabilities with ClipMind's AI-powered approach, the choice ultimately depends on your specific information organization needs and working style.
Google's tools serve adequately for simple, familiar mind mapping tasks within an existing Google Workspace environment. The learning curve is gentle, and for users who need basic diagrams without AI assistance, Google Drawings provides sufficient functionality. However, the fragmented workflow across multiple tools creates significant efficiency barriers for complex information organization tasks.
ClipMind represents the evolution of mind mapping for the AI era. By integrating webpage summarization, AI-assisted thinking, and dual-view editing into a unified environment, it addresses the fundamental challenges of modern information overload. The platform doesn't just automate manual tasks—it enhances cognitive processes through intelligent assistance.
For most knowledge workers dealing with complex information regularly, ClipMind's efficiency gains and quality improvements justify the modest learning investment. The ability to transform research into organized understanding in minutes rather than hours represents a paradigm shift in personal knowledge management.
If you're spending significant time organizing information manually across multiple tools, I recommend trying ClipMind's approach. The workflow efficiency gains become apparent quickly, and the quality of organized output often surpasses what's achievable through manual methods alone.
Learn More
- AI Mind Map Generator Review 2025: Top Tools for Visual Thinking
- How to Create Mind Maps from Webpages: Complete Guide
- Research Organization Tools: 8 Best Solutions for 2025
- Traditional vs AI Mind Mapping: Key Differences Explained
- Evaluating Knowledge Management Systems: Essential Criteria
FAQs
-
Can Google Drawings create proper mind maps? Google Drawings can create basic mind maps manually, but lacks dedicated mind mapping features like templates, automated layouts, or AI assistance. It requires complete manual creation of every element.
-
How does ClipMind's noise-free filtering work? ClipMind's technology automatically identifies and removes irrelevant webpage elements like advertisements, navigation menus, and promotional content, focusing only on the core informational content during summarization.
-
Is ClipMind compatible with Google Workspace? While ClipMind operates as a separate platform, it exports to formats compatible with Google Workspace, including images for insertion into Google Docs and Markdown for structured documentation.
-
What's the learning curve for ClipMind compared to Google tools? Google Drawings has a gentler initial learning curve due to familiarity and simplicity. ClipMind requires learning its AI features and interface but provides significant long-term efficiency gains that justify the investment.
-
Can I collaborate with others using ClipMind? ClipMind currently focuses on individual cognitive enhancement with AI collaboration rather than multi-user collaboration. For team-based mind mapping, Google's real-time collaboration features may be preferable.
-
How does ClipMind handle different types of web content? ClipMind's summarization works across various content types including articles, research papers, documentation, and blog posts. The AI adapts to different content structures to create appropriate mind map hierarchies.
-
What are ClipMind's export options compared to Google Drawings? Google Drawings exports primarily as images or PDFs. ClipMind offers multiple export formats including PNG, SVG, JPG for visual sharing, and Markdown for linear documentation and further editing.